HIPAA-compliant interoperability is about establishing a balance between smooth data exchange and maintaining strict adherence to HIPAA. Undoubtedly, interoperability has become necessary to provide enhanced patient care, helping hospitals join the collaborative care ecosystem.
However, this data transmission from one system to another includes major threats like potential data leakage or breach. But HIPAA compliance can help mitigate these concerns and ensure the secure transmission of data.
You might be thinking about how to do this, so let us tell you about HIPAA compliance. We will also discuss:
- Interoperability under HIPAA.
- Information accessible under HIPAA.
- Information that can be shared under HIPAA.
- How does HIPAA influence interoperability?
- What are patient rights and DUA?
At the end of the blog, we will highlight some use cases to help you understand the HIPAA application, so let’s get started!
What is HIPAA Compliance?
HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, which establishes guidelines for protecting patient-sensitive health information. Companies dealing with protected health information (PHI) must have a network and procedural security measures to ensure HIPAA compliance.
It is easy to ensure compliance with HIPAA-compliant software, which helps ensure data privacy and increases operational efficiency.
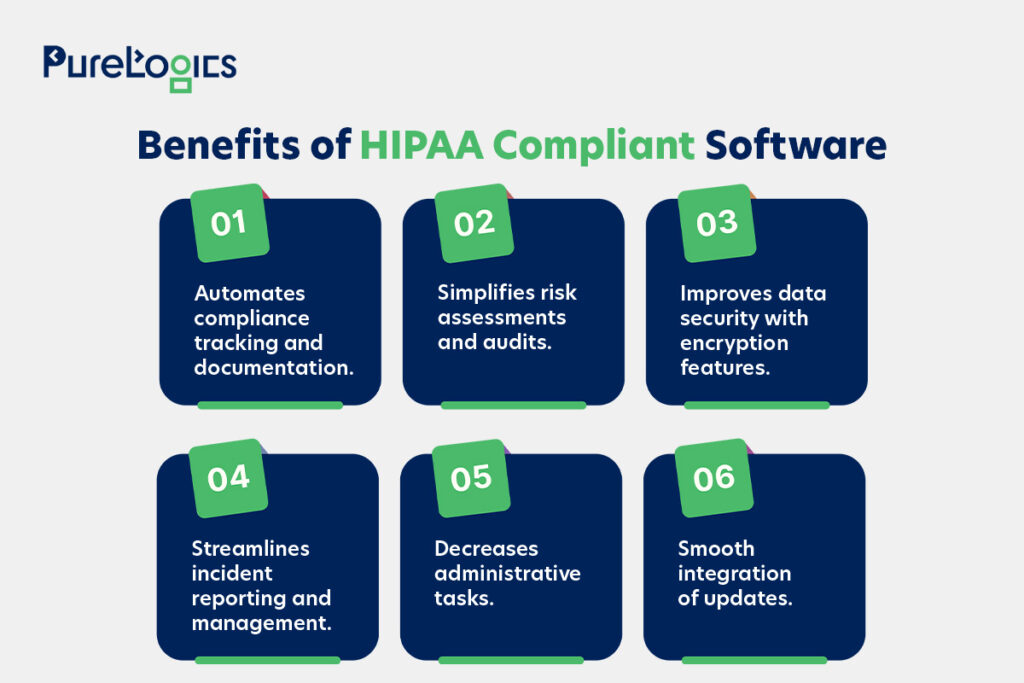
Besides the advantages mentioned above, the HIPAA is exceptionally useful in promoting healthcare interoperability, enabling efficient information exchange between systems and providers. However, guidelines for HIPAA-compliant mobile app development or web app development can help achieve HIPAA compliance.
What Does HIPAA-Compliant Interoperability Mean?
HIPAA-compliant interoperability means the smooth exchange of data between healthcare systems, while upholding the standards of security and patient privacy.
HIPAA provides the legal and technical foundation for safeguarding patient privacy while facilitating fast information flow between systems and providers.
It is essential in the development of healthcare interoperability solutions to prioritize HIPAA compliance and build data streams that follow the interoperability standards. This can also provide easy and secure access to data, strengthening patient trust.
Plus, the data that is not HIPAA-regulated can fall prey to cyberattacks.

Achieving interoperability can help improve care coordination by decreasing duplicate testing and ensuring faster access to critical health information, ultimately supporting better patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Some of the other advantages that can stem from interoperability under HIPAA are given below:
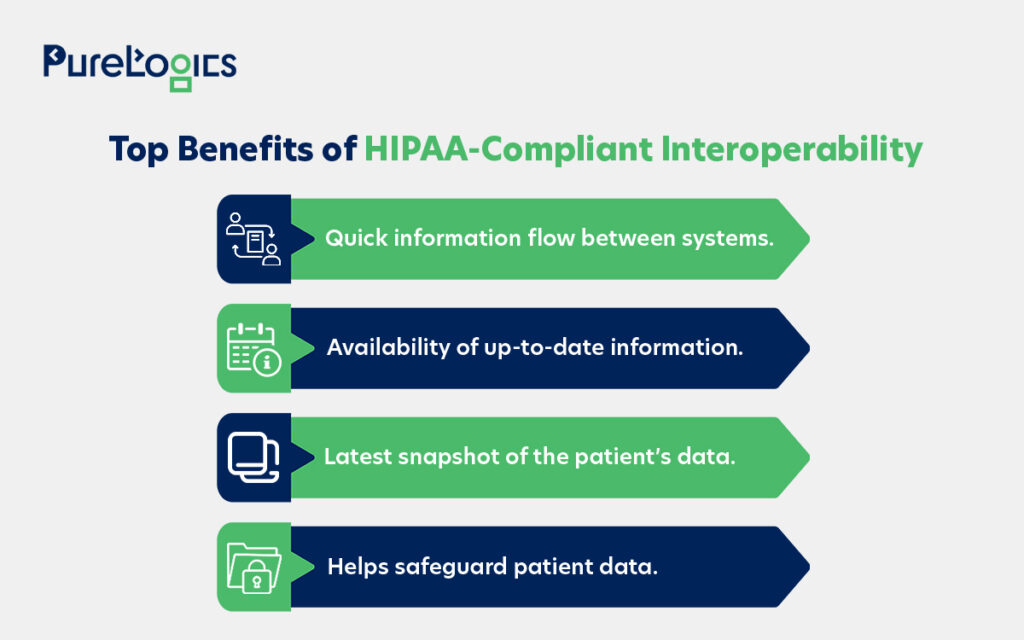
The HIPAA and FHIR integration offers healthcare professionals better risk management, enhanced data security, and streamlined processes. Not to forget the immense innovation potential, which can be used to benefit people. Like one of the HIPAA-compliant healthcare apps we developed for our client, Care on Demand.
CaringonDemand
Our team created a HIPAA-compliant iOS-based app that allows certified service providers to earn money by connecting with the people who need care within their vicinity. Going above and beyond, we also created a web app that allows patients to schedule and request care for a specific time and date.
- Safeguards patient and provider information during communication or appointment scheduling.
- Ensures that sensitive health data is transferred and stored according to HIPAA requirements.
- Supports real-time matching between caregivers and recipients, enhancing access in healthcare delivery.
With around two decades of experience, PureLogics has healthcare IT professionals adept at developing HIPAA-compliant software. If you are looking to build healthcare software, then book your free consultation here.
Let us tell you more about how HIPAA specifically addresses interoperability. Our experts have narrowed it down for you because it is vast in scope.
How HIPAA Influences Interoperability?
HIPAA is wide in scope, and we have narrowed it down to how it changed healthcare information technology regarding interoperability.
Before HIPAA, there was no accepted set of security standards for the protection of healthcare information. The system operated on an old paper system, but when the industry transitioned to electronic records. The potential security risks also heightened.
The HHS (Department of Health and Human Services) built regulations that safeguard the security of patient records. It published the HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules to meet these requirements.
- The Security Rule safeguards the health information held or transferred in electronic form and highlights procedural safeguards that organizations must implement to secure their electronic protected health information (ePHI) for individuals.
- The Privacy Rules showcase national standards to secure health information.
The HIPAA supports secure healthcare interoperability and ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and access to electronic health data via strict privacy and security rules.
Also, the covered entities, such as insurers and hospitals, are required to apply administrative and technical safeguards to prevent unauthorized access and data leakages.
All in all, HIPAA promotes trust in digital healthcare systems and improves compliance across the healthcare industry. Here’s how the HIPAA privacy rules help.
HIPAA Privacy Rules
The Privacy Rule applies to covered entities (who work with patients) such as clinicians, hospitals, and business associates. Such as lawyers, transcriptionists, and pharmacy administrators.

These rules establish the standards that protect health information.
- It prohibits the uses and disclosures of information that might be made without patient authorization. However, patients can do whatever they want with their records.
- Paper, oral, and electronic records can be counted as protected health information (PHI). The PHI should be transferred and shared securely.
- It also highlights who has to safeguard the PHI and emphasizes that only minimal health information can be shared between entities.
Next are the security rules, which focus on implementing administrative controls. Below, we are discussing this in detail.
HIPAA Security Rules
It is a set of legal standards for the maintenance, confidentiality, and availability of PHI in the United States. It requires healthcare entities and business associates to implement administrative and technical safeguards to protect patient data and mitigate risks of data breaches. The noncompliance with HIPAA security can cause data breaches, resulting in fines and legal repercussions. So, below we are explaining the rule’s core standards in detail.
- The administrative safeguards point out the policies and procedures for security measures and how to conduct the security risk assessments. It also defines the roles and responsibilities for building emergency plans.
- Physical safeguards highlight the device security standards, including physical access to health information security and its infrastructure, and more.
- The technical safeguards explain the technologies required to secure ePHI against unauthorized access, disclosure, access controls, encryption, authentication, and secure transmission.
The data exchange under HIPAA is all about secure transmission, storage, and placing control in the patient’s hands. And it also underlines the information that should be accessible.
HIPAA-Compliant Interoperability: What Info Must Be Accessible?
HIPAA introduced the concept of a designated record set (DRS), which includes
- Medical records.
- Billing data.
- Health plan claims information.
Basically, any record used by covered entities in making decisions about an individual is included in DRS. The designated record sets are mentioned in laws after HIPAA. For instance, the Cures Act now mandates that entities share records with patients electronically, not just on paper.
HIPAA-Compliant Interoperability: When Info Can Be Shared?
The HIPAA privacy rule highlights three conditions where providers can share health information without patient consent. These three conditions are given below:
- Treatment.
- Payment.
- Healthcare operations.
Your doctor or hospital can access your information under HIPAA if they use it to treat you, enhance their internal operations, or get payment for services. Otherwise, they are out of luck without the patient’s permission.
Of course, there are exceptions, but generally HIPAA prohibits access to information and allows it to be shared only under specific circumstances and for justified reasons. These activities are essential for any entity that wants to procure healthcare data. They have to inform about the Purpose of Use, also determining who can obtain data.
The HIPAA data sharing also includes exchanging health information, often requiring a HIPAA data use agreement (DUA) when the data is not fully de-identified. The DUA ensures that the data is utilized only for permitted purposes (healthcare operations, public health, or research).
HIPAA-Compliant Interoperability: What Should be Included in a Data Use Agreement?
The data use agreement (DUA) must contain the following pointers to achieve HIPAA compliance.
- Define how the recipient (such as a researcher) will use and share the dataset, consistent with the research purpose. The agreement should not include any disclosure that can breach the HIPAA Privacy Rule if the disclosure is made or done by the covered entity.
- Limits who can use the data and requires the recipient to use appropriate safeguards to protect data and not disclose data other than permitted use.
- Report disclosed information to the covered entity, agents, or subcontractors to whom the recipient provides information and agrees to the same restrictions.
All the above-mentioned things are not enough to become a master of HIPAA-compliant interoperability. You need to know about the patient’s rights, too.
What Are the Patients’ Rights in HIPAA?
HIPAA gives patients rights such as the right to examine and obtain a copy of their health records and demand corrections. Some of the other rights HIPAA offers patients are given below:
- Request access to copies of their medical record.
- Ask for corrections to be made in their health records.
- Receive notice explaining how their health information might be utilized.
- Decide if they want to consent before their health information can be used.
- Receive a report on the reason, when, and why their health data was shared.
Within HHS, the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) exercises the responsibility for enforcing rights, which effectively helps in promoting HIPAA-compliant interoperability.
Furthermore, let us tell you about the use cases in which HIPAA compliance is necessary.
HIPAA-Compliant Interoperability: Use Cases
The scenarios in which HIPAA compliance becomes essential are given below:
- Secure Data Transfer
Healthcare institutions often need to share sensitive data with other individuals or entities. This is challenging due to HIPAA rules, but a healthcare software development company can help you develop a HIPAA-compliant solution that ensures secure data transfer.
- Remote Consultation
With the rise in remote consultations, organizations need HIPAA-compliant telehealth platforms. That facilitates the secure sharing of sensitive information to collaborate effectively.
Rise of Telehealth

- Research Collaboration
Researchers often require the sharing of sensitive data for collaborative projects. This can be highly challenging due to privacy protection and compliance with HIPAA regulations. Therefore, platforms that ensure the secure transmission of data are required.
- e-Prescription Software
The e-Prescription software must be HIPAA compliant to handle electronic protected health information (ePHI) securely. It should include safeguards like encryption, access controls, and audit logging for patient data protection.
We developed an e-prescription software that addresses the specific needs of telemedicine providers and patients. With separate logins for doctors and patients, an easy-to-use interface is compatible with each device.
- Secure Communication & File Sharing
Healthcare institutions often require the sharing of sensitive patient data with external entities or need to share large files. This can be challenging due to HIPAA regulations emphasizing the secure transfer of information so that only authorized individuals can access it.
- Secure Data Access and Migration
Hospitals or clinics need to give partners and employees secure access to data. It also allows for protected data migration, aligning with HIPAA regulations. These two things can be challenging for organizations. But taking the help of experienced healthcare IT professionals, you can easily mitigate these challenges.
Wrap Up
HIPAA-compliant interoperability is the foundation for building trust in digital healthcare. It isn’t just about compliance, it’s about delivering care when and where it is required the most.
At PureLogics, we have spent nearly two decades developing HIPAA-compliant healthcare software solutions that truly help patients and healthcare professionals. From on-demand healthcare platforms to data sharing systems, our healthcare IT professionals ensure that compliance doesn’t come at the cost of privacy and security.
If you want to build a HIPAA-compliant web or mobile app from scratch or enhance it, then book free expert consultation here.


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 June 16 2025
June 16 2025