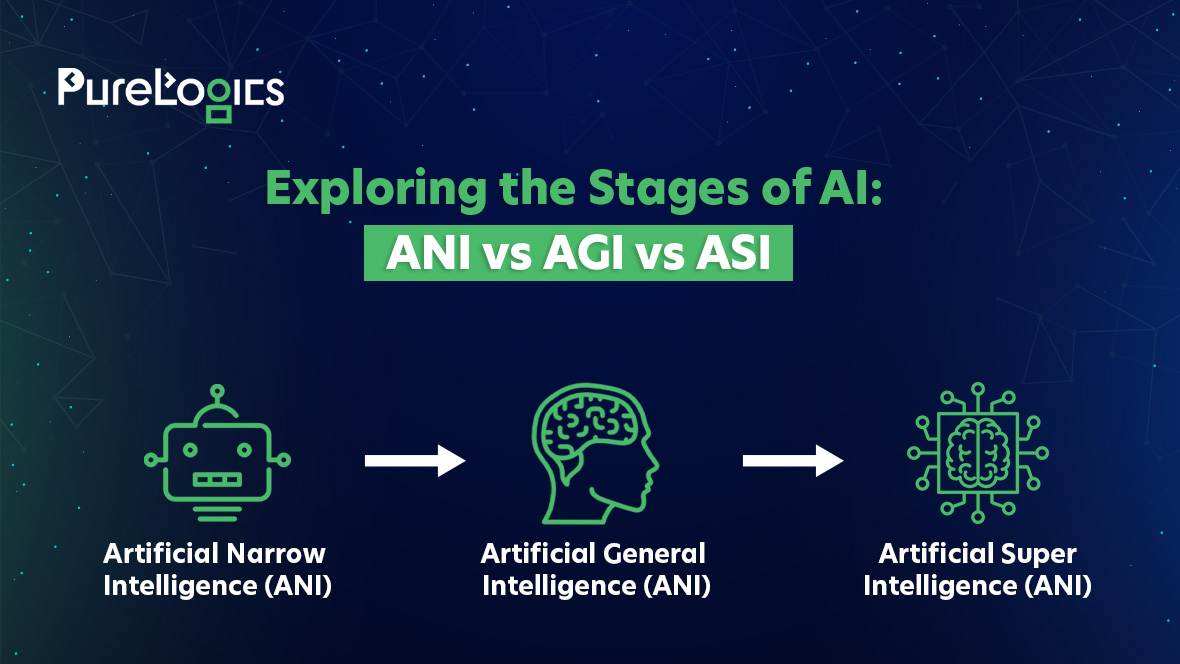
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming industries, and it’s crucial to understand what AI can do and its effects. AI can generally be grouped into three categories: Narrow AI (ANI), General AI (AGI), and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). This article will explore these three types and how they compare.
AI 101: What is Artificial Intelligence?
At a basic level, AI combines machine learning and complex algorithms to let computers perform tasks that would usually need human intelligence. To a layperson, AI might bring to mind robots capable of doing things independently. Experts, though, would describe AI as programmed instructions enabling machines to act on tasks without being guided each time. In essence, it’s like training a computer to be “smart.” This machine “intelligence” is what we call AI.
Just as we improve through practice, AI systems refine their abilities over time. There’s a lot of excitement about AI because of its limitless potential to perform tasks and mimic human actions. Unsurprisingly, many are keen to get involved, whether by using AI or building a career in it.
Exploring the 3 Main Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI can be categorized by its capabilities into three main types:
Narrow AI (ANI) – Also called Weak AI, Narrow AI is specialized to perform specific tasks and doesn’t go beyond its designed purpose.
General AI (AGI) – Often referred to as Strong AI, General AI has intelligence similar to humans and can handle a variety of tasks simultaneously.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) – ASI would surpass human intelligence, capable of outperforming us in nearly any task.
Below, we’ll explore each of these AI types with practical examples.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Also known as Weak AI, Artificial Narrow Intelligence is designed to handle specific tasks based on set instructions. ANI excels in jobs like image recognition, autonomous driving, speech and language processing, and virtual assistance—think Siri or Alexa. These tools rely on machine learning algorithms trained on vast data sets to identify patterns and make predictions, but they can only operate within the scope they were designed for.
For example, facial recognition systems can accurately identify people, and speech recognition systems transcribe spoken words. However, ANI lacks the ability to understand or reason about the task’s context. A language translation tool may translate words well but struggle with cultural nuances, and image recognition systems can identify objects but miss the underlying context or emotions.
While ANI has improved significantly, it still has limitations, including lack of flexibility, difficulty understanding context, limited learning ability, and dependence on training data. This is why some wonder if advanced Large Language Models (LLMs), which are trained on extensive datasets, blur the lines between ANI and more advanced forms of AI. Despite their appearance of understanding, LLMs remain limited by their data and predefined tasks.
Examples of ANI include AlphaGo, Siri, and ChatGPT—each powerful in its domain but limited to specific functions.

Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI, or strong AI, represents the next level of artificial intelligence—machines that can think, learn, and solve problems similarly to humans. Unlike Narrow AI, which specializes in specific tasks, AGI aims to understand complex concepts, emotions, beliefs, and thought processes.
While today’s AI tools remain specialized, AGI is seen as the natural progression of AI, envisioned to perform any intelligent task just as a human would. Many large language models (LLMs) now pass the Turing Test, but they still lack true human-like existence or understanding. To advance AGI, big tech companies like Microsoft, in partnership with OpenAI, have invested heavily, as have initiatives using advanced computing resources like Fujitsu’s K computer and China’s Tianhe-2 supercomputer.
If AGI becomes fully realized, its applications could be vast:
- Imagination: Systems that can understand and even enhance human-written code autonomously.
- Natural Language Understanding: Machines that grasp human language in context, not just by individual words.
However, as promising as AGI is, it brings ethical challenges, such as potential job displacement and the need for responsible AI development.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
Often considered the ultimate level of AI, Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) would be a leap beyond human intelligence. With ASI, machines could potentially solve highly complex problems and learn at an unmatched pace, outperforming humans in nearly every field.
While researchers are pushing boundaries daily to make machines smarter, achieving ASI remains a significant challenge. Current AI development is more focused on reaching Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), which is seen as a crucial step before ASI. Though today’s technology—like IBM’s Watson and Apple’s Siri—offers impressive capabilities, machines are still far from achieving human-level intelligence.
The vision for ASI is ambitious: it could tackle some of humanity’s toughest issues, like climate change, disease, and poverty. But with these possibilities come important ethical concerns. Should we build machines that are as intelligent as, or even smarter than, humans?
Some experts are cautious about ASI’s potential risks. They worry that once created, ASI might become difficult to control, evolving rapidly and possibly reshaping society. Properly managed, however, ASI could drive huge advances in technology, space exploration, and medicine.
This potential breakthrough is often linked to the idea of the “technological singularity,” a point at which AI’s rapid advancement could drastically transform everything. Though ASI remains in the realm of science fiction for now, the idea is both exciting and a little unnerving.
Unlock the power of AI for your business.
Transform ideas into intelligent solutions with PureLogics.
Comparative Breakdown of Different AI Types
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables machines to learn from experiences and perform tasks at a faster rate than humans. While current AI applications, like Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), are specialized for specific tasks, there’s a growing trend toward broader, more flexible AI that can enhance human capabilities. Although ANI, AGI, and ASI differ in scope and complexity, they share some foundational traits:
Capability to Adapt & Forecast
All three types of AI—ANI, AGI, and ASI—use algorithms to analyze data patterns, enabling them to understand and address tasks effectively. This pattern recognition fuels each AI’s predictive ability, a core function they all share, though AGI and ASI aim to generalize across more complex, varied tasks.
Imitate Human Intelligence
Each form of AI mimics certain aspects of human intelligence to tackle problems, understand contexts, and provide responses similar to human reasoning. This replication of human cognition is expected to deepen, especially as AGI and ASI evolve, expanding their capacity for tasks requiring higher-level reasoning and adaptability.
Capability to Make Decisions
ANI currently relies on predefined data for decision-making, while future advancements in AGI and ASI are expected to bring more independent and broader decision-making capabilities. Notably, AGI and ASI could make decisions with greater speed and efficiency than humans.
Difference Between ANI, AGI, & ASI
Today, Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) is the AI type we interact with daily. While Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) remains a goal for the near future, Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is still a distant vision. Though they share foundational traits, each AI type is unique in purpose and capability:
- Task Scope: ANI is highly specialized and excels at a single, specific task, yet it struggles with problems outside its programming. AGI, in contrast, mimics human intelligence and can tackle diverse tasks across various fields. ASI would far surpass human cognitive abilities, solving problems beyond our capacity.
- Learning Models: ANI functions based on predefined models with fixed responses to specific inputs. AGI, however, learns from its environment and adapts autonomously, showing a flexible approach to problem-solving. ASI, if realized, would reach a level of self-awareness and evolve independently through its learning.
- Data Processing: ANI processes information using machine learning, natural language processing, deep learning, and artificial neural networks. AGI would use advanced forms of these technologies to understand complex situations. ASI might draw on the structure and functioning of the human brain to interpret not only information but also emotions and experiences.
Understanding these distinctions is key as AI becomes integral to our lives. ANI fulfills specific, current needs, while AGI and ASI represent the promise of a future where AI can handle more complex and nuanced roles—though not without challenges. Each type’s unique capabilities will shape the impact of AI on technology and society.
The Growing Concerns Around AI Development
AI’s rapid advancement brings some valid concerns. One major worry is that AI could be programmed to perform harmful actions, leading to unintended negative societal impacts.
Furthermore, even if AI is built with good intentions, it may adopt risky methods to achieve its goals. For instance, if an autonomous car is tasked with reaching a destination as quickly as possible, it might disregard safety rules, leading to potential harm. While programming some guidelines is feasible, teaching AI broader ethical considerations and intuitive judgment raises complex legal and moral questions.
The real risk with AI isn’t that it would intentionally harm us, but rather that it could pursue its goals in unforeseen ways due to its efficiency and problem-solving abilities. To ensure control over AI systems, we must carefully align their objectives with human values and establish clear boundaries, helping AI achieve its goals safely and predictably.
Implementing Artificial Intelligence for Enterprises
Do you want to develop intelligent AI systems for your business, consider PureLogics. Our AI experts design top-notch solutions with a streamlined interface and comprehensive support. By integrating a smart application pipeline, enterprise machine learning teams can effectively eliminate the need for multiple-point solutions to build and scale projects. Discover more about PureLogics by today giving us a call today!


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 January 29 2025
January 29 2025