Is your healthcare system HL7-compliant? If not, then you are putting the lives of your patients at risk. As a hospital owner or a healthcare professional, you might have encountered this term often. But do you know about its importance and its widespread impact?
Today, approximately 95% of hospitals in the US use it; if you are not utilizing it. You are missing out on all its advantages, like high interoperability, access to patient history, and streamlined communication and workflows.
Consider this: It is your time to build or integrate an HL7-based system, and this blog is a guide to help you understand its evolution and different versions, as well as how to introduce it in your current systems. So, keep on reading to make your system HL7-friendly in no time.
Let us first tell you what it is and how it has evolved.
What is HL7?
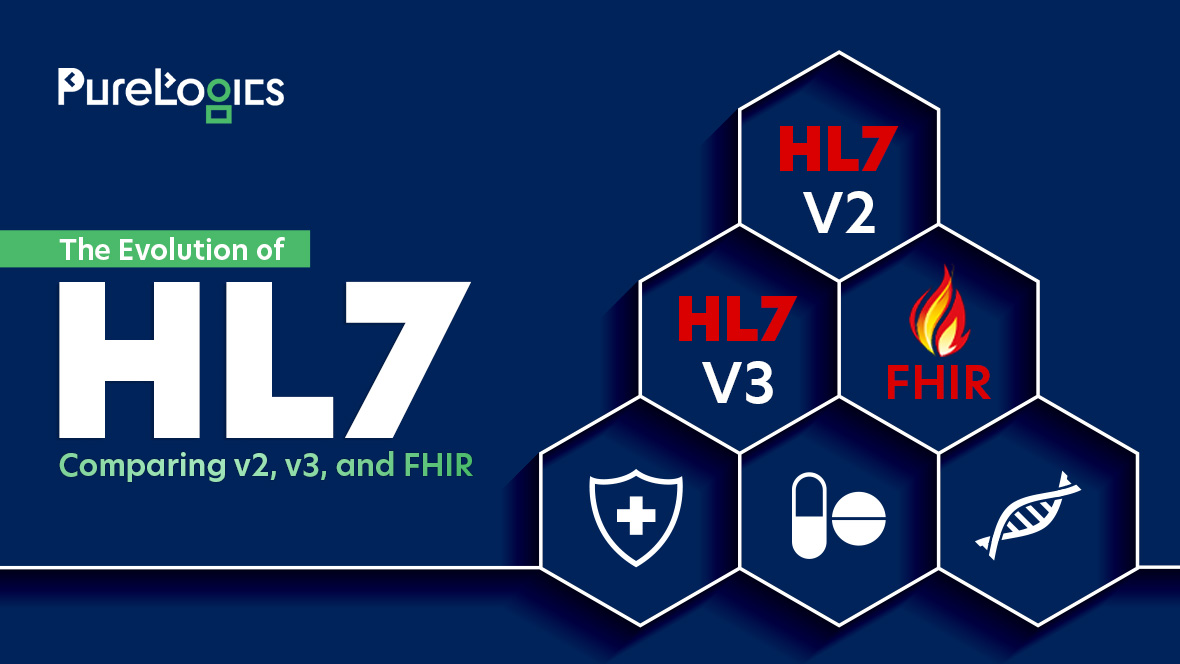
Health Level 7 (HL7) is a set of international clinical standards and messaging formats used to exchange data between healthcare systems. Health Level Seven International (HL7), a healthcare standards organization, develops and maintains these standards. It has created different versions:
- HL7 v2
- HL v3
- HL7 CDA
- HL7 FHIR
Most of the versions are widely used for integrating, receiving, and transferring data.
Interoperability and HL7
Interoperability is a crucial aspect of modern healthcare, allowing providers to exchange data efficiently. HL7, on the other hand, is the most widely used healthcare standard for attaining interoperability by offering a consistent and structured way to share data. The healthcare data interoperability market is expected to reach $533.92B by 2034.
With time, its different versions have been released to cater to the growing needs of healthcare.
Evolution of HL7
The evolution began with the release of HL7 Version 1 (v1) in the late 1980s, a prototype that did not gain widespread adoption.
Later, the HL7 Version 2 (v2) was released in the 1980s and became dominant. Afterwards, the HL Version (V3) introduced a more structured approach. The latest one is FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resource), which focuses on simplicity and modern web technologies.

Why is HL7 used?
The communication between different types of software in the healthcare sector was difficult before, and below are the reasons why this standard became popular:
1. Interoperability
Hospitals and clinics around the globe use different software programs developed in other languages and offer various functionalities.
For instance, a medical research institute uses software different from a hospital’s. Often, these types of institutions need to exchange data about patients, and this standard enables healthcare organizations to create uniform data that anyone with access can retrieve and use in their systems.
2. Automated workflows
Implementing an EHR (Electronic Health Records) system is expensive, and this standard helps optimize how data is exchanged between devices. It provides recommendations for automating standard workflows, which helps decrease labor and operational costs.
3. Customizable
It allows some customization (such as the addition of optional fields and the ability to add message segments).
For example, healthcare organizations develop apps according to their needs, and this standard allows the developers to create interfaces for data exchange between different healthcare organizations instead of changing their software.
This standard has evolved with time according to the needs of the healthcare institutes. Let’s see its different versions.
Versions of HL7
Below are the different versions to view and choose which is best for your systems.
HL7 v2
HL v2 was introduced in the 1980s to facilitate the exchange of message-based healthcare data. It was the first healthcare standard that gained widespread popularity to streamline communication between various healthcare apps, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), laboratory systems, and billing systems.
Key Features of HL7 v2
Some of the key features of HL7 v2 are given below:
- Message-Based Communication: Utilizes delimited text messages with separators like pipes (|) and carets (^).
- Event-Triggered Exchange: Data is exchanged in response to specific events such as patient admissions or lab results.
- Flexible: Its flexibility enables customization to meet specific organizational standards.
Challenges
Here are the challenges of this version:
- Inconsistencies leading to a lack of standardization.
- Dependence on custom implementations for different healthcare providers.
- Complex integration with modern web-based technologies.
The v2 is divided into 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.3.1, 2.4, 2.5, 2.5.1, and 2.6. Each version added more features, message types, and structure improvements, making the standards more powerful and complex. The v2.3.1 and v2.5.1 are the most widely used.
HL7 v3
It was introduced in the early 2000s with the primary purpose of standardized healthcare data exchange. v3 focuses on a more structured and standardized approach and was built on the Reference Information Model (RIM), which provides a unified framework for representing healthcare data.
Key Features of HL7 v3
Some of the key features of v3 are given below:
- Model-Driven Approach: Utilizes RIM to ensure consistency.
- XML-Based Messaging: More structured in comparison to v2, enhancing data clarity.
- Enhanced Data Consistency: Decreases the variability witnessed in v2.
- Covers Various Domains: It supports electronic healthcare records (EHR), pharmacy, clinical documents, etc.
Challenges
Some of the challenges associated with v3 are:
- The implementation is complex due to the RIM-based approach.
- The transition from v2 to v3 is difficult.
- The v3 has limited adoption due to its complicated nature.
HL7 CDA
The CDA (Clinical Document Architecture) is an electronic standard Health Level 7 (HL7) built for clinical data exchange. This XML-based standard highlights the structure and semantics of clinical documents such as discharge summaries, procedure reports, etc. Additionally, it adheres to V3 ITS (Implementation Technology Specification) built on the HL7 Reference Information Model (RIM) and uses V3 datatypes.
Key Features of HL7 CDA
The critical features of the CDA are given below:
- Readable: It is readable, highly flexible, and expressive.
- Detailed Information: It contains detailed information objects like images, sounds, and multimedia.
- Default Context: Sets the default context for its content (can exist in a non-messaging context).
Challenges
The challenges associated with CDA are:
- Complexity in ensuring data accuracy.
- Integration challenges with legacy systems
HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resource)
The FHIR standard states how healthcare information can be exchanged between different systems regardless of its storage. It was introduced in 2014, and its primary purpose is API-driven modern healthcare data exchange.
The reason behind the creation of FHIR was to overcome the limitations of v2 and v3 while including modern web technologies.
Key Features
The key features are given below:
- Flexibility: FHIR is developed around resources, which are individual data elements representing specific concepts like lab results or patient medications. These resources can be combined and utilized in various contexts, offering flexibility.
- Interoperability: FHIR is built with interoperability in mind, and it standardizes how healthcare data is formatted and transferred, maintaining constant communication across multiple systems.
- Support for Multiple Formats: FHIR supports multiple formats (like JSON and XML), allowing developers to select the format that fulfills the user’s needs.
- Strong Community: It supports the community of developers, IT professionals, and clinicians. This community-driven approach brings ongoing improvements.
Challenges
Some of the challenges related to FHIR are given below:
- Security and privacy concerns.
- Scalability problems.
- Integration with legacy systems is complex.
Let’s do an HL7 FHIR comparison with other versions, as it is the latest version.
Comparison of HL7 v2 vs v3 vs FHIR and CDA
The v2 is for a legacy system that does not cover the problems related to interoperability and data storage. It also has an outdated approach that does not facilitate scalability and is impossible to read except for non-V2 experts.
However, v3 is an effort to develop an electronic healthcare model with XML-based messaging. It introduces the RIM (Reference Information Model) concept and offers data types, terminologies, and messages. Furthermore, the FHIR focuses on the open-standard paradigm; unlike previous standards, it is available for study and use.
All in all, the popularity of the standard hugely depends on its access. Below is the table highlighting the brief differences of all standards released by the HL7 organization to attain interoperability.
| Feature | HL7 V2 | HL7 V3 | HL7 CDA | FHIR |
| Overview | It is an older standard for data transfer between systems. | Highly complex data exchange standard. | Defines a clinical document’s structure. | Modern data exchange structure. Flexible data elements and web-based approach. |
| Interoperability | Limited. | Complex to achieve. | High interoperability (Best for document exchange). | High flexibility. |
| Data Format | Text, pipes (|), and hats (^) based messages (pipes separate different fields in a message and hats separate parts inside fields. | XML-based. | XML document-oriented. | XML, JSON, RDF-based. |
| Implementation | Lower complexity due to simplicity. | High complexity. | Moderate. | Implementor-friendly. |
| Adoption Rate | Highly used in legacy systems. | Very low. | Moderate. | Growing rapidly. |
| Resources (technology availability) | It offers enterprise-level interoperability and is used to exchange data between systems within an organization. | RIM implementation is mandatory, making it complex. | A mandatory component of data exchange in healthcare. | Easy for web-savvy developers, and may require time and additional help from FHIR experts. |
There is no universal choice between these standards, and the differences between HL7 versions suggest their utility for each type of user. However, before you decide to go with any standard, just analyze your system on these basic points given below:
- Your needs or requirements.
- The existing infrastructure of your institution.
- Your long-term goals.
If you are still confused about which version best goes with your systems, let us give you some use cases suggesting how hospitals use it.
Use Cases of HL7 Standards in 2025
It has a broad spectrum of applications in healthcare, and its use cases continue to evolve in 2025. Below are some of the key examples:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR)
It allows smooth data exchange between various EHR systems, enabling healthcare providers to access patients’ medical data, including medications, allergies, and lab results, regardless of where they are. This detailed view of patient data offers better-informed clinical decisions.
- Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
This standard supports the efficient and reliable transfer of lab results between LIS and EHRs, decreasing manual mistakes, minimizing turnaround times, and enhancing the accuracy of lab data.
- Radiology Information System (RIS)
It allows the radiologists to quickly access and share data by streamlining the flow of radiology images and reports. This efficient access can speed up diagnoses and treatment decisions.
- Pharmacy System Integration
It allows the pharmacies to connect with EHR systems, allowing accurate medication orders and enhancing communication between pharmacists and providers. This can help increase patient safety by decreasing medication errors.
- Public Health Reporting
This helps by facilitating the electronic submission of public health data, such as immunization records, etc. This automated reporting enhances timeliness and data accuracy, supporting public health initiatives.
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS)
The integration helps the CDSS to access patient data from various sources, offering clinicians real-time insights and recommendations to facilitate swift decision-making.
- Patient Scheduling Systems
It simplifies appointment scheduling and management across various healthcare services.
- Telehealth Services
This standard facilitates the exchange of information between EHRs and telehealth platforms, aiding in remote consultations, care delivery, and monitoring. This integration increases access to healthcare services, especially for patients in remote areas.
- Health Information Exchange
It allows for the swift and secure exchange of healthcare data between different healthcare organizations. This interoperability gives healthcare providers access to a comprehensive view of health information.
In addition to these use cases, the HL7 integration leverages APIs to connect healthcare systems. They offer a standardized way for different apps to exchange data and communicate. However, integrating it or building an HL7-based system can pose specific challenges.
Key Challenges of HL7 Integration
Integrating HL7 or building an HL7-based software can be complicated and expensive due to the complexity and variety of healthcare systems. One major issue is interoperability between different systems, as HL7 messages may be formatted differently across platforms. Data mapping between legacy systems and newer technologies can also be time-consuming and cause errors.
Additionally, data privacy during the exchange of sensitive health information is also a significant concern.
However, healthcare software developers with years of experience can help you with the integration or development of HL7-based software. With around 19+ years of experience, we have been helping healthcare professionals with the development of HIPAA-compliant HL7-based software as per their needs.
Key Challenges of HL7 Integration

Overcoming the above-mentioned challenges requires careful planning, robust systems, and continuous collaboration between healthcare providers and IT professionals. The ineffective mitigation of these challenges can lead to data leakage or non-compliance, which can also cause heavy fines.
If you are facing any of the challenges mentioned above, then contact our team and tell them what you need. With experience of 50+ healthcare projects, they have got you covered!
Become HL7 Compliant
You can have HL7-based software, or our integration experts can integrate it into your systems, considering your system conditions or requirements. Enhancing the interoperability of your system, helping you provide the best patient care.
With around two decades of experience, our healthcare IT professionals have worked with global teams to make their systems HL7 compliant.
Contact our experts, let them know your needs, and get your free quote today!


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 June 2 2025
June 2 2025