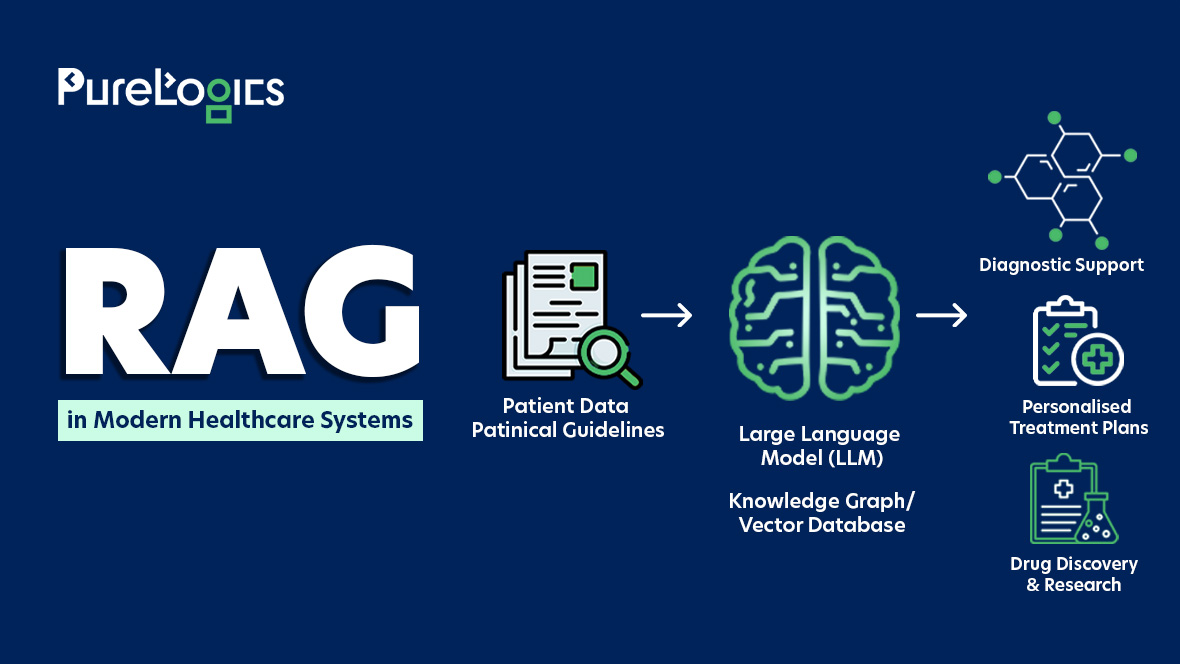
As more clinics and hospitals go digital with EHRs, PMS, telemedicine, and other digital platforms and tools, one issue that persists is healthcare interoperability, which focuses on the secure exchange of patient data across systems to enable coordinated care.
But despite advances in healthcare technology, many systems can’t share data smoothly, resulting in delayed care, repeated testing, and even medical errors. The strict compliance standards and regulations also make data exchange more difficult. However, efficient care depends on accurate and timely data exchange, and that’s where interoperability can play a huge role.
Let us tell you all about interoperability and how you can achieve it in six steps. But we are starting with the basics about the introduction of healthcare interoperability and why it matters.
What is Healthcare Interoperability?
Interoperability in healthcare means secure and timely access, use, and integration of electronic health data so that it can be utilized to improve the health outcomes of patients.
Here, just think about your work systems together. You might use an HMS (Hospital Management System) that your staff uses to manage internal data across departments, EHRs that patients cannot access, and a standalone billing software. When all these systems are interoperable, they can exchange data internally and with other hospitals. An organization can adopt an industry-standard data format or establish clear metadata formats to achieve interoperability.
Importance of Data Interoperability in Healthcare
The importance of data interoperability in the healthcare world cannot be denied in today’s interconnected world. Below are a few ways in which it can help an organization.
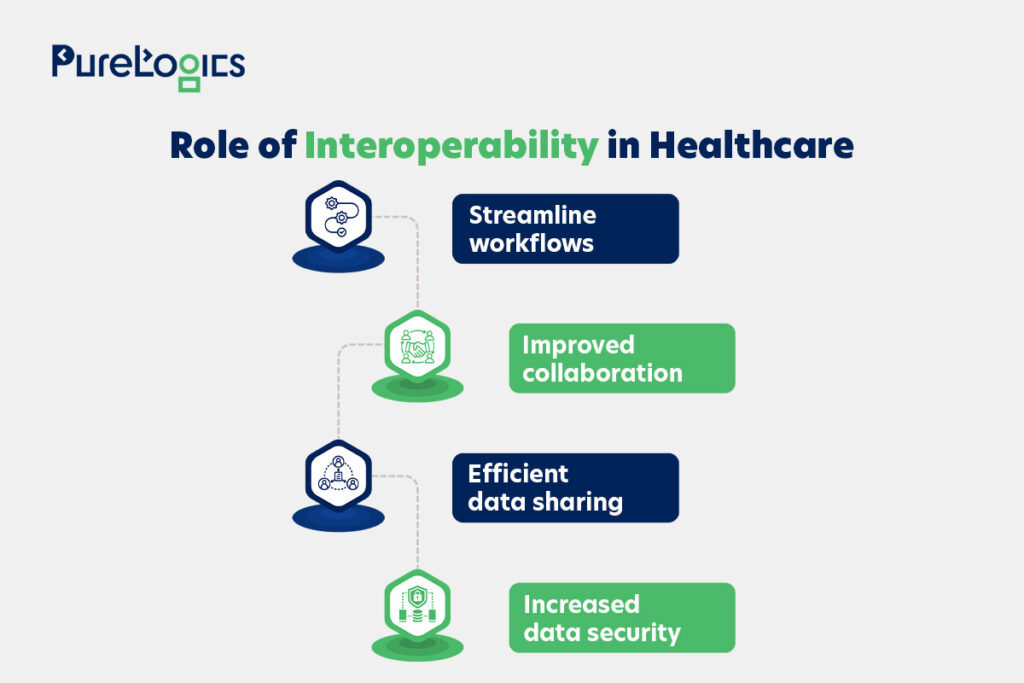
Assuredly, interoperability holds the key to efficient and improved patient care, and below are some more reasons why it matters the most in this interconnected world of technology.
Why Does Healthcare Interoperability Matter?
The data is not only crucial for efficiency in healthcare, but it is also about life-saving decisions. Because when healthcare professionals have quick and secure access to medical history. Like lab results and other critical information, they can make better decisions. In contrast, when the data is siloed or fragmented, the results can be detrimental to patients’ health.
For instance, consider a patient who relocates to a new state and switches healthcare providers. And the patient’s healthcare records are incompatible with the new provider’s system. Resulting in the denial of access to vital information such as prior treatments, allergies, or ongoing conditions, leading to a delay in proper treatment or mistakes.
That’s why hospitals are moving towards developing healthcare interoperability solutions.
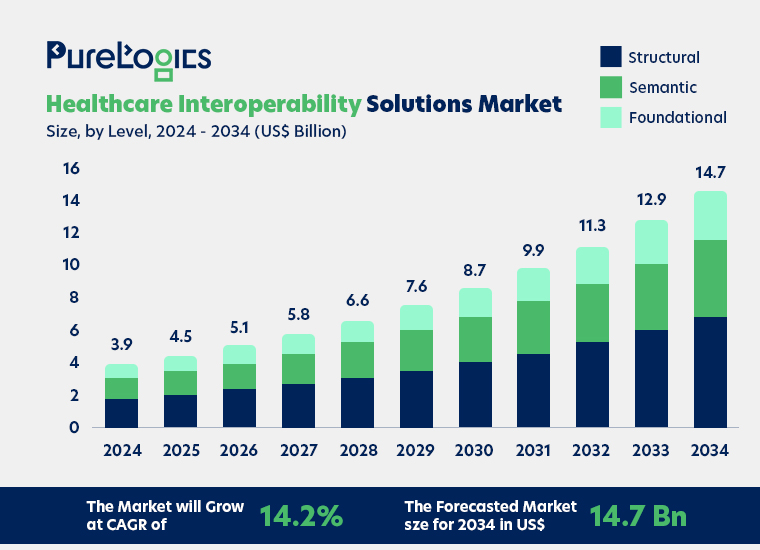
Source: Market.us
These solutions are growing to fix inefficiencies like duplication of tests and procedures, which inflate the healthcare costs and burden the already overloaded healthcare system. Below are some of the top ways in which interoperability can be beneficial for the healthcare systems as a whole.
Healthcare Interoperability Benefits
Some of the top benefits of interoperability are given below:
- Improved Care Coordination
Clinicians and healthcare professionals have easier access to patients’ data, which can lead to fewer mistakes, no repetition in tests, and no miscommunication.
- Enhanced Performance
The combined data can be analyzed more easily, which means interoperability helps organizations study data trends and make data-driven improvements.
- Improved Experiences
Data interoperability can decrease the amount of redundant data both within and outside an organization.
Indeed, interoperability in healthcare systems is essential, and interoperability standards are crucial in achieving it. Let us tell you all about it.
What are Interoperability Standards in Healthcare?
Interoperability standards in healthcare can be stated as guidelines and protocols that allow different healthcare systems and apps to share data.
These standards ensure that information can be understood by different systems (regardless of their location or architecture).
The key healthcare interoperability standards, including HL7 and FHIR, are given below.
- Health Level Seven (HL7)
It is a set of international standards for sharing, integration, and retrieval of electronic health information. HL7 standards make sure that disparate systems can communicate with each other efficiently.
- Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR)
FHIR is the standard for the electronic exchange of healthcare information developed by HL7. It ensures easy data sharing and integration by the utilization of modern web technologies and data formats such as XML and JSON.
- Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine (DICOM)
It makes sure that the imaging systems from different operators/manufacturers can interoperate. DICOM is the standard for storing, transmitting, and retrieving information related to medical imaging.
- Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT)
SNOMED CT is a standardized way to represent clinical content in EHRs, ensuring that the meaning of health information is the same across different systems.
- International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
Globally, ICD codes are used to classify diseases and health conditions. This standardization of diagnostic information helps in data accumulation, analysis, and sharing.
Interoperability can be achieved on different levels, and companies can benefit from each level by sharing basic health information. Some of the levels are easy to achieve, while others can require additional development.
What Are Healthcare Interoperability Levels?
Interoperability for healthcare has four levels that have been explained by informatics experts and the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS).
Also, the USCDI (United States Core Data for Interoperability) establishes data elements of the data that need to be interoperable. These standards offer the technical requirements to make data exchangeable. Below are the four interoperability levels:
Healthcare Interoperability Levels

- Foundational
Defines the basic standards mandatory for one system or app to communicate with another safely. It is also known as simple transport, and in truth, it is the most basic level. For instance, a clinician downloads the PDF file of the patient’s latest lab results from the lab’s results portal, then enters the data manually into the patient’s health record.
- Structural
Explains the organization, format, and syntax of data sharing. When structural interoperability is achieved, all the data is standardized to a particular format, making it easy for multiple devices or systems to interpret. In this level, the data is arranged in a set format so that the system receiving it can automatically identify specific data fields.
Data standards like FHIR and HL7 offer structural interoperability so that records are consistent and can be easily transferred between systems.
- Semantic
This level allows the interpretation and understanding of data for clinical decision-making. It involves the exchange of data between systems with entirely different data structures.
For example, there are many specialized DICOM and non-DICOM formats for images, and with semantic interoperability, images can be transferred from one system to another. And can be interpreted and incorporated into the new system, irrespective of the original image format or source. However, determining what data to transfer or collect can be complex.
- Organizational
Enables the timely healthcare data exchange between organizations or individuals with various requirements or standards. At the same time, keeping in view the organizational, legal, and policy parameters. So, to achieve this level of interoperability, there must be governance or policy innovations and technological advancements to ensure consent and security.
Achieving interoperability is important, especially for data security and privacy.

So, below are the steps to help you ensure interoperability.
6 Steps to Achieve Healthcare Interoperability
Below are the six steps that can help you achieve interoperability, and the first step is focused on defining goals.
- Define goals
You can start by analyzing which kind of data you need and want to share and who should have access to it (doctors or labs, etc).
- Analyze Your Systems
Evaluate your existing systems like EHRs, billing systems, and other software.
- Integrate APIs
Build or integrate APIs to help your systems seamlessly connect and exchange data.
- Implement Interoperability Standards
Use global standards (FHIR or HL7) so your data is formatted in a way the other systems can easily read.
- Test and Secure Systems
Make sure to test the data flows to assess the safety and HIPAA compliance.
- Ongoing Support
Ensure to monitor and then scale the system as the needs grow.
Following all these steps can be overwhelming, and a mistake in just one step can lead to security and compliance issues. So, the best strategy over here is to contact a healthcare software development company. As they have experience in developing HL7 or FHIR-based solutions. Attaining interoperability in complex and busy healthcare systems is not that easy, and it is your right to know the challenges you can face.
The Challenges of Interoperability in Healthcare
Some of the core challenges in healthcare data exchanges are given below:
- Data Silos and Legacy Systems
Today, many healthcare providers rely on legacy systems that are not designed to communicate with one another. These old systems are the reason behind creation of data silos making it difficult for information to be shared across different departments. Many organizations consider the cost and complexity of a system revamp to be high. However, in reality, the revitalization of legacy systems can enable interoperability, saving organizations from installing additional systems to encourage coordinated care.
- Data Security and Privacy
One of the biggest challenges associated with interoperability is data privacy. Indeed, healthcare data is among the most sensitive types of personal data, and breaches can have disastrous consequences. Moreover, the HIPAA compliance requirement adds more complexity to achieving interoperability. Because the data sharing practices must be designed to secure privacy while enabling the efficient exchange of information.
- Cost of Integration
The cost of integrating new systems can be high to meet the standards of interoperability. Especially for small businesses and startups that often operate on tight budgets, which means patient care is prioritized over IT overhauls.
These challenges in no way mean that interoperability is unachievable. Below you can find solutions to all challenges related to interoperability.
Solutions to Healthcare Interoperability Challenges
Although there are challenges, the solutions below can help you overcome the barriers to achieve full interoperability.
- Adoption of APIs and Microservices
APIs allow various software applications to communicate with each other even when they are not originally meant to. With API implementation, the healthcare organization can develop a bridge between legacy systems and newer platforms without any need for complete system renewal. Also, microservices can break down monolithic systems into smaller and manageable components. This modular approach allows healthcare providers to upgrade the individual parts instead of disrupting the entire system.
- Utilization of Cloud Technology
The cloud-based platform helps healthcare providers share, store, and access patient data in real-time. While ensuring that the data is properly encrypted and secure. Also, the cloud platforms often come with built-in interoperability features, enabling the systems to share information easily.
- AI and Machine Learning Implementation
Machine learning and artificial intelligence, in addition to transforming the technology world, hold the potential to solve complex interoperability challenges. By intelligently parsing (breaking down) the unstructured data into usable formats.
- Tools and Technologies
The technologies and tools given below can also help in the smooth implementation of data interoperability.
- Data integration tools: These tools can automate the process of extracting, transforming, and loading data between systems.
- Metadata management solutions: They allow the development, storage, and management of metadata, offering context and enabling data discovery.
- API management platforms: Help in designing, deploying, and managing APIs to allow scalable and secure data exchange.
By using these tools, the organization can speed up its interoperability initiatives and remove technical barriers to data exchange.
- Partnerships
Interoperability cannot be solved alone, and it requires strong collaboration between healthcare organizations, technology vendors, and regulatory bodies. To generate a universal set of solutions and standards.
Data interoperability is one of the necessary needs of the healthcare industry, and its importance in improving patient care cannot be denied. But still, the healthcare world is unable to match the pace of interoperability in comparison to other industries.
Current State of Healthcare Interoperability
Even though the need for healthcare interoperability cannot be denied but the healthcare industry still needs to catch up with other industries. In terms of smooth and efficient data exchange. The reasons behind this slow pace are:
- Complexity of healthcare data, for instance, formats like lab results and unstructured data like the notes of physicians.
- Different types of software and platforms (EHR, PMS, etc).
But the industry has witnessed progress with Health Level Seven (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resource (FHIR) implementation. However, this implementation has been uneven, and leveraging the advantages of these standards becomes difficult due to the high cost.
Yet there are IT vendors or healthcare software developers who are developing cost-effective, interoperable solutions to further decrease the data sharing complexity.
Key Interoperable Solutions 2025
Some of the key interoperable solutions this year are given below
- Data Quality and Semantics: Solutions that focus on harmonizing data and ensuring accurate sharing of data are emerging.
- AI-Based Solutions: These are being utilized to improve data extraction and streamline the workflow to bridge the gap between modern technologies and legacy systems.
Final Thoughts
Healthcare interoperability is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern and patient-centered care. It allows smooth sharing of critical healthcare data across various systems. Helping the providers make informed decisions. Despite ongoing challenges like the presence of legacy systems and data complexity, the industry seems to be making progress, especially with the development of innovative interoperable solutions. Such as FHIR or HL7-based platforms and cloud-based APIs, are making it easier to connect with systems and promote standardized data exchange.
At PureLogics, we specialize in developing HIPAA-compliant, HL7 and FHIR-based interoperable systems tailored to your needs. Contact our healthcare IT experts today to transform how your organization handles healthcare data. Or build a secure, scalable, and seamless solution with us.


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 May 19 2025
May 19 2025