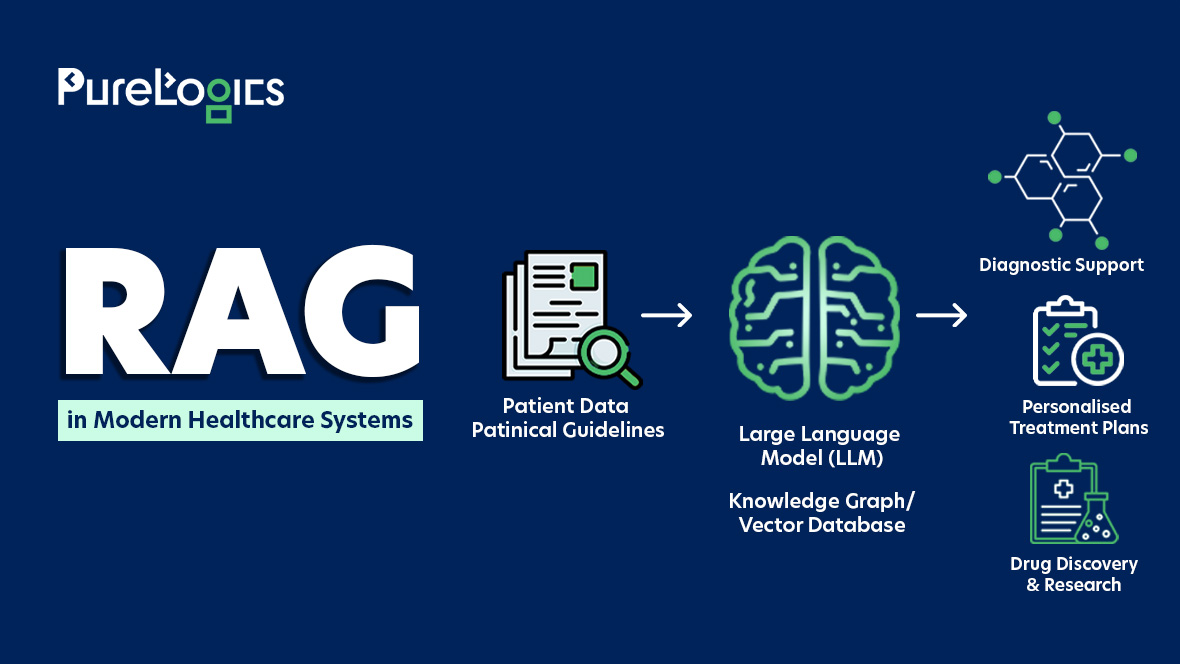
HIPAA compliance is all about protecting patient data and privacy from secure storage to safe transmission. But let’s be honest: becoming (and staying) HIPAA compliant is not that easy.
Especially with the 2025 changes, which has made compliance feel like a maze of rules and regulations. Indeed, it’s challenging but not impossible. That’s why in this blog, we are providing a detailed checklist and practical tips to help you stay on the right side of HIPAA.
But first, let’s take a look at the latest developments in HIPAA for 2025.
What is HIPAA Compliance in 2025?
HIPAA (The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) establishes rules for the protection of sensitive patient data. It highlights that organizations handling protected health information (PHI) should have security networks in place to ensure compliance. The HIPAA laws are also necessary to:
- Modernize healthcare information flow.
- Explains how personal identifiable information (PII) should be maintained by healthcare organizations and insurance agencies.
- Discusses limitations on healthcare insurance coverage (such as coverage continuation despite job changes, etc).
You might have noticed its widespread application, but let’s clarify who HIPAA applies to.
Who does it apply to?
HIPAA was passed in 1996 to make healthcare delivery more efficient and applies to:
- Covered Entities: Any organization accessing protected personal health information (PHI), including health plans, hospitals, clinics, physicians, dentists, health insurance organizations, and pharmacies etc.
- Business Entities: This includes third-party service providers that transfer, receive, and transmit ePHI for covered entities. For instance, IT contractors or cloud storage providers, etc.
What are the New HIPAA 2025 Updates?
Last year, on December 27, the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) at the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) released a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM).
The aim was to modify the HIPAA Security Rule to fortify the cybersecurity measures for electronic protected health insurance (ePHI). It has gone into effect on March 7th, 2025, following the comment period.
To ensure HIPAA compliance, these updates bring significant changes to the way healthcare organizations handle patient data and privacy.

Let us tell you all about these updates so that you can ensure or check your compliance with HIPAA.
- Mandatory Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
The 2025 HIPAA Security Rule mandates the implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across all access points to ePHI. This requires the users to confirm their identities using multiple credentials, such as passwords, biometric data, and security tokens, before accessing sensitive systems. The need for enforcement of MFA arises from the escalation in cybersecurity threats, which can help hospitals mitigate the risk of unauthorized access even when an authentication factor is breached.
- Improved Data Encryption Protocols
The updated regulations emphasize encryption for electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI), both at rest and in transit. This move from optional to compulsory encryption highlights the strong response to cyber threats targeting the health sector. Therefore, health organizations are required to use advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive data (both when stored and when being transferred).
- Implementation of Security Controls
The sharp distinction between “required” and “addressable” security controls is removed. Previously, this differentiation provided flexibility in security measures (based on unique circumstances), catering to diverse operational needs. Also generating inconsistencies in ePHI protection. Now, the call for uniform implementation of all security controls aims to eliminate such disparities, guaranteeing a constant defence against the rising cybersecurity threats.
- Asset Inventories and Network Maps
This requirement ensures that all the devices, applications, and systems interacting with ePHI are monitored. Now, organizations need to develop and maintain inventories of their technological assets and a comprehensive map of their electronic systems. Also, the regular updates to these maps and inventories (at least annually) are necessary to maintain the strengthened security. Hence, reinforcing compliance and patient trust with regulatory standards.
- Audits On an Annual Basis
Healthcare organizations must conduct and document detailed audits once every 12 months. These audits should be about administrative, technical and physical security measures.
This move represents a shift in how data security is handled, essentially going from just reacting to problems to staying constantly alert. Encouraging healthcare organizations to strengthen their security protocols and adopt a proactive risk management approach.
- Vulnerability Scanning
All the covered entities and business associates are now mandated to perform vulnerability scans. At least every six months, and conduct penetration tests annually. Identifying any loopholes or vulnerabilities in their systems.
Other than compliance, this shift urges organizations to have a mindset where every security test is considered a diagnostic tool.
The widespread adoption of technologies (AI/ML, etc) in healthcare has made HIPAA implementation necessary now more than ever. Let’s discuss this more in detail.
Why is HIPAA Compliance More Important Than Ever Before?
With the rise in data breaches, organizations must make compliance their priority to ensure patient trust. Let’s tell you about common HIPAA violations that can cost you heavy fines and push you into an unending spiral of penalties:
- Accessing PHI without authorization.
- Failure to conduct a comprehensive organization-wide risk assessment.
- Insufficient or inadequate ePHI access control.
- Absence or lack of a risk assessment strategy.
- Inadequate ePHI access control.
- Failing to apply encryption.
- Missing risk assessment strategy.
- Unlawful disclosure of PHI.
Even HIPAA-compliant healthcare mobile apps are necessary. Below are some examples of HIPAA non-compliance that cost organizations large sums of their finances.
Examples of HIPAA Violations
HIPAA compliance is vital for hospitals and healthcare institutions in protecting patient information. But non-compliance can result in the imposition of huge fines, resulting in a loss of finances. For instance:
The Guam Memorial Hospital Authority (GMHA) Incident
The GMHA was fined $25,000 after two separate cybersecurity incidents. HHS received a complaint about attacks and launched an investigation in 2019, during which another complaint was received in March 2023. This second complaint was about the two former employees gaining unauthorized access to GMHA network systems.
Warby Parker Incident
Warby Parker was fined a $1.5 million penalty for HIPAA breach. This cyber attack occurred in 2018 and affected nearly 198,000 people.
There are two categories of punishments in terms of HIPAA non-compliance. Let us tell you about that too in detail.
Types of HIPAA Violations
HIPAA non-compliance or violations can result in financial penalties known as civil monetary penalties (CMP). The other are criminal penalties, particularly involving wrongful disclosure.
Civil Monetary Penalties (CMP).
Authorities issue these penalties to ensure compliance with regulations and safeguard the privacy and security of sensitive patient information.
| Tier | Violation Type | Penalty Range Per Violation | Annual Maximum (Repeat Violations) |
| 1 | Lack of Knowledge | $100-$50,000 | $25,000 |
| 2 | Reasonable Cause Not a willful neglect | $1000-$50,000 | $100,000 |
| 3 | Willful neglect Corrected within 30 days | $10,000-$50,000 | $250,000 |
| 4 | Willful neglect Not corrected within 30 days | $50,000-$1.5M | Not specified |
The HHS can consider factors such as history of prior compliance, the size of the covered entity, the impact of the violation, and the financial condition to determine the entity’s level of violation.
Moreover, the HHS may reduce the penalties in good-faith cases, and this policy is known as Notice of Enforcement Discretion. This allows the OCR (Office for Civil Rights) to exercise its power to reduce penalties in certain circumstances. Such as a business associate or a covered entity has made a good-faith effort to comply with HIPAA regulations. Or it’s failure to do so because of certain circumstances beyond its control.
The next one is criminal penalties, which are mainly imposed due to wrongful disclosure.
Criminal Penalities
These are imposed on entities that do not follow HIPAA compliance standards and are responsible for the wrongful sharing of PHI (Protected Health Information). Based on severity, there are three tiers of criminal penalties:
| Tier | Violation Type | Penalty Range per Violation | Repeat Violations |
| 1 | Unknowing wrongful PHI disclosure | $100-$50,000 | $25,000 |
| 2 | Wrong Disclosure (Under False Pretenses) | $1000-$50,000 | $100,000 |
| 3 | Pretenses with Malicious Intent (to harm or benefit yourself) | Severe penalties, including jail | Case-dependent |
The HIPAA violations can be found in multiple ways, including investigations, complaints, and proactive enforcement initiatives by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR). Also, via regular audits conducted by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
So, to escape the fines or penalties mentioned above, you have to follow the rules highlighted by HIPAA. Let us help you understand those easily.
Rules of HIPAA Compliance
The HIPAA rules and regulations are there to protect the confidentiality and privacy of ePHI (electronically protected health information). Furthermore, the HIPAA rules also give patients rights regarding their healthcare information.
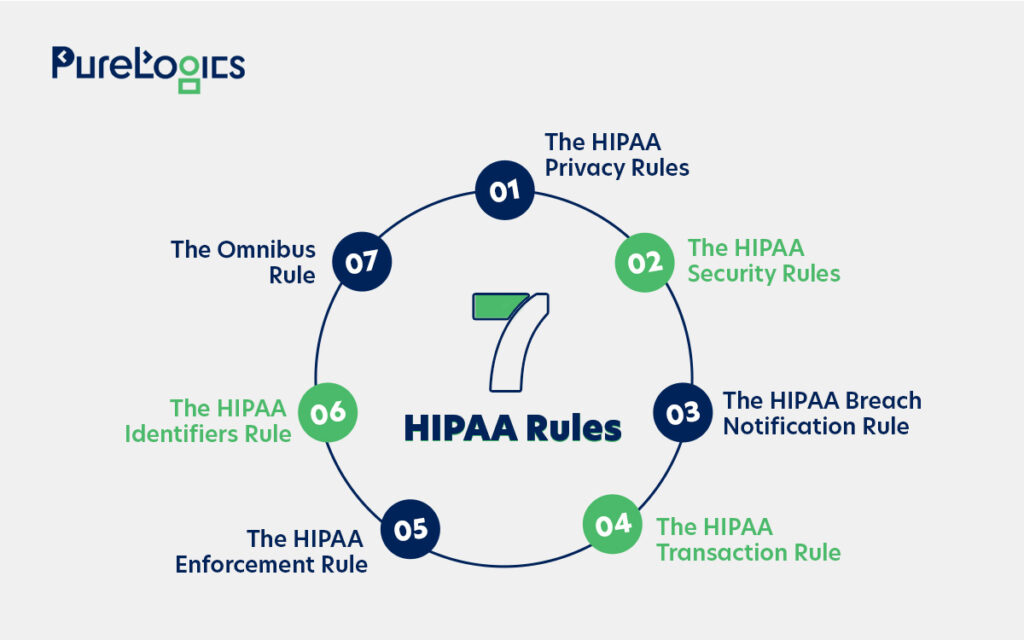
Below are the 7 HIPAA rules explained in detail to help you escape any kind of fine.
- HIPAA Privacy Rule
This rule puts in place the national security standards for protecting patients’ rights to PHI. It applies to covered entities only and emphasizes that the patient must receive a file for the HIPAA release form.
- HIPAA Security Rule
It’s a nationwide standard for safeguarding the use, transmission, and storage of ePHI. This rule is for covered entities and their business associates.
- HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
It obligates the businesses on how to respond in case of a data breach and provides guidelines on reporting the breach.
- HIPAA Transaction Rule
It emphasizes taking essential cybersecurity measures (for business entities and healthcare services) to safeguard ePHI while other transactions are performed.
- HIPAA Enforcement Rule
This was introduced so that businesses face necessary penalties for data breaches related to civil or criminal laws. It also makes reporting of security and privacy breaches mandatory.
- HIPAA Identifiers Rule
It was introduced to ensure that organizations share PHI only with authorized entities. Each organization should have a unique identification number so that PHI is only disclosed to entities recognized under HIPAA.
- Omnibus Rule
It created new rules for reporting data breaches to help strengthen existing controls.
These rules are there to enhance the protection of sensitive health information and to make sure that organizations take stronger measures to protect their data.

Indeed, HIPAA compliance is all about responsible data use and secure patient data rights. So below, we have compiled a checklist that can help you ensure your HIPAA compliance.
HIPAA Compliance Checklist 2025
Below is the checklist that can help you assess your compliance easily. All you have to do is analyze your security systems with the points given below.
Administrative Safeguards
- Do you have a designated Privacy Officer for overseeing compliance with HIPAA regulations?
- Do you have a set of formal written policies and procedures to address how PHI is used, stored, and shared within your organization?
- Do you conduct risk assessments regularly to identify potential vulnerabilities related to the privacy of PHI?
- Do you have an incident response plan for managing and reporting security breaches or HIPAA violations?
- Do you perform regular background checks for employees handling PHI?
- Do you regularly update or view policies?
- Do you have clear procedures and guidelines for granting, modifying, and revoking PHI access?
- Do you document the steps taken to correct non-compliance issues?
- Do you offer mandatory HIPAA training for all employees handling PHI?
- Do you have Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) in place with all vendors and third parties who have access to PHI?
- Do you have a breach notification policy in place that explains how to handle incidents involving PHI breaches?
- In case of a breach, do you have plans to notify affected individuals within 60 days?
- Do you report breaches to HHS (Department of Health and Human Services) when applicable?
Physical Safeguards
- Do you have secure areas to safeguard PHI, preventing unauthorized access?
- Have you restricted access to areas (using keycards or other security measures) where PHI is stored?
- Do you ensure that paper records containing PHI are locked away securely?
- Are your portable devices containing PHI secure?
- Do you dispose of physical records containing PHI securely?
- Do you track the flow of PHI in your organization?
- Do you have policies for the remote handling of PHI?
Technical Safeguards
- Do you use encryption to protect PHI during transmission?
- Have you ensured a role-based access to ePHI?
- Have you implemented multi-factor authentication (MFA) for ePHI access?
- Do you regularly audit access logs to identify any unauthorized access?
- Do you have a secure backup plan to protect ePHI?
- Do you regularly update or patch your software?
- Do you utilize communication channels such as HTTP and FTP to receive or send PHI across networks?
Other than this checklist, we also have some tips that can help you stay secure and compliant.
Top 7 HIPAA Compliance Tips
Here are the top seven tips that can help you stay compliant with HIPAA.
- Educate Yourself
If you are looking to become fully compliant, then familiarize yourself with the three main components of HIPAA, which are the privacy rules and violations.
- Safeguard Your Physical Documents
Although digital records have become increasingly common in healthcare, they have not completely replaced physical documents. So you must ensure that all paper files containing patient records are stored securely in locked rooms or cabinets accessible only to authorized personnel. However, it is best to store your records digitally to increase their security.
- Password Protection
Remember, passwords are your first defense against unauthorized access to electronic health records (EHR) or other sensitive systems. Just make sure to follow these rules when you are creating a password for your system:
- Use a minimum of 8 characters.
- Avoid sequential characters (e.g., 1234).
- Don’t use repeated characters (e.g., bbbb).
- Strong Encryption: Think Beyond Passwords
Laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices can get lost. So, encrypting these devices can add a layer of extra security, and in case of theft, the encryption makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized users to access patient information.
- Utilize secure Email Services
Most companies don’t know this, but sending healthcare information via regular email is a significant HIPAA violation. Instead, use secure email services that offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring that only intended recipients can access the email contents.
Pro Tip: Verify the recipient’s email address before sending private/confidential information.
- Stay Updated on HIPAA Regulations
Always stay on top of HIPAA regulations to ensure your organization remains bulletproof in terms of compliance and data privacy. Because the HIPAA regulations are evolving with the transformation of technology.
- Report Suspicious Activity Immediately
Immediately report any suspicious activity or potential breaches to your organization’s designated HIPAA privacy officer or compliance team. Because the early detection and prompt reporting can help you prevent any further damage.
Wrapping Up
Staying ahead of HIPAA compliance is not just about escaping penalties but about safeguarding the trust and privacy of every patient you serve. As new updates bring new expectations around privacy protocols and trust, now is the best time to check your systems to ensure their compliance.
If you are looking for a scalable solution, then at PureLogics, we specialize in developing
HIPAA-compliant software solutions. Whether you are upgrading your existing system or want to start from scratch, our experts have got you covered.
Get in touch with our team to learn how we can develop a HIPAA-compliant solution tailored to fit your needs.


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 May 12 2025
May 12 2025