The dilemma every enterprise faces is how to handle the growth without breaking the bank or compromising user experience. It is a fact that when your application suddenly needs to serve 10x more users, you have two choices: either invest heavily in powerful servers (that may fail under pressure) or design an app that can scale by the addition of more instances, which is termed horizontal scaling. It makes apps more scalable and reliable, thus allowing enterprises to grow without worrying about their solutions.
Let us tell you more about horizontally scaled apps and how you can develop them to support your enterprise growth. We are beginning with the intro of horizontal scaling so that you can understand the concept and advantages of horizontally scaling an app.
What Is Horizontal Scaling?
Horizontal scaling involves adding nodes or machines to the infrastructure to meet the organization’s changing demands. Imagine your current infrastructure is a rack of servers working together. However, your existing system fails to meet the expected needs or reaches its capacity limits. To address this, the solution involves deploying additional complete server units through simple resource upgrades.
In simple terms, horizontal scaling involves expanding your resource pool by adding more machines rather than enhancing the existing ones. This technique is beneficial as it provides better fault tolerance and unlimited expansion potential through distributed workload across multiple independent servers.
Now that you understand the concept of horizontal scaling, let’s give you the definition of horizontally scaled apps.
What Is a Horizontally Scalable App?
These are apps that are designed to handle the increased load by adding more servers or instances. They are typically stateless, enabling them to run identical copies behind a load balancer. This model supports elastic growth, high availability, and fault tolerance. In short, multiple instances of an app run; each instance handles some of the user requests, and the load balancer distributes requests among instances.
It is like distributing workload among several employees instead of one, allowing businesses to accommodate an increasing workload easily. Furthermore, scaling horizontally can be advantageous for apps that require flexibility and agility.
What Are the Benefits of Horizontal Scaling Your App?
It is a key strategy for improving system capacity and performance. Here’s how it can help your company ensure uninterrupted services.
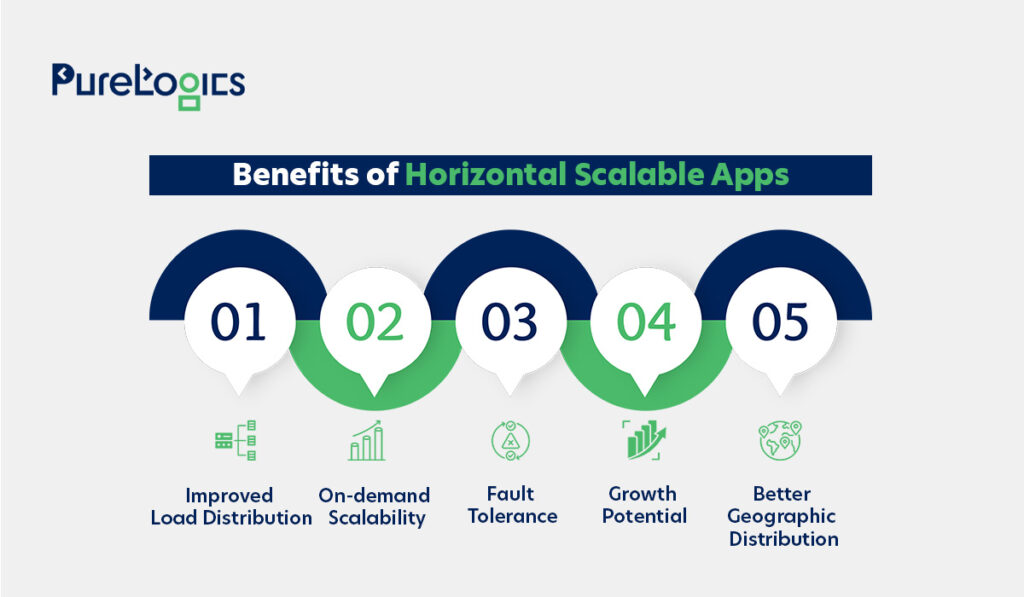
Improved Load Distribution
These apps distribute the workloads across multiple app instances. This leads to better resource usage, system reliability, and efficient response times under heavy traffic.
On-Demand Scalability
The apps can be scaled horizontally by launching more service instances in real-time to handle spikes in demand. It enables businesses to respond flexibly to changing workloads without any need for costly infrastructure upgrades.
Fault Tolerance
In horizontally scaled apps, when one instance fails, others continue to cater to the user requests. This built-in redundancy ensures high availability and minimal downtime.
Growth Potential
The best thing about these apps is that they are not dependent on hardware capacity. By adding more nodes or containers, the continuous growth of an app can be ensured, helping the business meet the changing market demands.
Better Geographic Distribution
Application instances can be deployed across multiple regions or data centers. It helps decrease latency for end users, enhances user experience, and facilitates data compliance needs.
Beyond these compelling benefits, horizontal scaling offers distinct features that can help you stand apart from your competitors.
What Are the Features of Horizontal Scalable Apps?
Horizontally scaling can bring a multitude of advantages for businesses. Some of the top features that make it possible are given below:
| Features | Details |
| Concurrency | These apps support the parallel execution of multiple requests or tasks by using multiple service instances. |
| Load balancing | Load balancers such as NGINX, AWS, and ELB divide incoming requests equally across available application instances. In this way, resources are fully utilized and the performance remains stable. |
| Resilience | Application instances are stateless and interchangeable. In case of failure in one instance, the others can continue to serve. This built-in redundancy enhances fault tolerance and system availability. |
| Auto-scaling | Application platforms like Kubernetes or cloud services can scale app instances based on memory, request count, ensuring efficient use of infrastructure. |
No doubt, horizontal scaling brings a range of advantages. But it’s smarter to assess whether your app truly needs it. Over the past decade, we’ve identified clear signs in apps that were held back by poor scalability. Our team helped scale them horizontally, and now they’re thriving. Here are those signs so that you can spot them early, too.
Signs You Need a Horizontally Scalable Application
So, the signs we have promised are present below for you to read! First, assess your app as per these signs and then make any decision.
- Your app slows down during peak traffic.
- The single server is unable to handle the number of concurrent users.
- The app has independent modules with uneven traffic.
- Your app’s performance declines when running on multiple processes/threads.
- You need high availability all the time and cannot afford downtime.
- You want your app to be accessible across multiple geographic regions.
If your app has all or four to five signs mentioned above, then it’s time to scale your app and let us tell you how to scale it horizontally.
How To Design A Horizontal Scalable App?
Below are some steps that can help you scale your app horizontally.
Design Stateless Services
The first rule of horizontal scaling is to make the services stateless. This means that services do not store session data or local state. Any server instance can handle any request, and this can be achieved by utilizing external systems like Redis or DynamoDB to store session data. Furthermore, use JWT tokens for authentication instead of in-memory sessions. Also, avoid writing to local disk and use cloud storage or shared volumes.
Break App into Microservices
It is better to break the system into microservices, each responsible for carrying out individual functions. This allows the scaling of functions that are required to be scaled; for instance, your payment service might need more instances than the admin panel. This can be done by defining clear boundaries around services. Furthermore, for synchronous calls, use REST APIs or gRPC, and for better decoupling, use a message queue, e.g., Kafka, RabbitMQ, for async communication.
Add Load Balancers
You need to add load balancers to distribute traffic because your services are stateless and broken up. You can use NGINX, HAProxy, or cloud-based load balancers like AWS ELB or GCP Load Balancer. In addition to this, make sure to configure health checks to route traffic only to healthy instances and set up auto-scaling rules to launch additional instances during traffic spikes.
Use Scalable Databases, Caches, and Queues
It is also important to scale the data layer, as centralized databases can become bottlenecks. So you need to use distributed databases, caching layers, and message brokers to handle large volumes of data and communication. For distributed data storage, consider using Cassandra, MongoDB, or DynamoDB. For frequent caching of accessed data, add Redis Cluster or Memcached. To queue tasks and decouple services, use Kafka or RabbitMQ.
Automate Deployment, Monitoring, and Scaling
After making your architecture scalable, it’s time to make it manageable, which means:
- Automating deployments
- Monitoring your system’s health
- Allowing infrastructure to respond automatically to demands
You can use Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, or Amazon ECS for container orchestration, and monitor your services with Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK Stack. Additionally, ensure that auto-scaling groups are enabled, which scale services based on CPU usage or queue length.
Although the development of horizontally scalable apps might seem easy, it requires careful consideration of the steps mentioned above. But any discrepancy can lead to the app malfunctioning, which can result in increased vulnerability and loss of customers.
Key Challenges in Building Horizontally Scalable Applications
Development of horizontally scalable applications offers many advantages, but also comes with technical challenges such as:
- Managing application state requires making the app stateless.
- Proper traffic distribution can be complex, and any discrepancy can lead to overloading of specific instances.
- Monitoring and debugging issues become complicated in a distributed environment.
- Controlling infrastructure costs while scaling efficiently can be a challenge, too.
Wrapping Up
Horizontal scaling can help you manage high traffic loads on a budget. But incorrect balancing of load or improper debugging can lead to the malfunctioning of the app. This can cause customers to bounce back from your website, resulting in lost profits and falling behind in the market competition.
Confused? Consult an App Development Expert Before Taking Any Decision!
Before making any decision, ensure to consult app development experts. Here’s what they can do for you:
✔Evaluate your app’s scalability needs and identify bottlenecks.
✔Recommend the right tools for load balancing and distributed data.
✔Suggest best cloud practices and how your app can grow efficiently.
With their expertise, you can avoid costly mistakes, build resilient and scalable systems, and cater to 88% (Think with Google) of online consumers who leave other websites due to a bad experience.
If you are interested, then we are offering a 30-minute free consultation with our development experts. You can trust us because we have:
- 20+ years of experience years of experience.
- Completed 1300+ projects across retail, insurance, health, finance, real estate, and education.
You don’t have to do anything, just book an expert consultation with us today.
FAQs
How to scale an application horizontally?
If you are looking to scale an application horizontally, then deploy multiple instances of the app across different servers or nodes. Also, use a load balancer to distribute traffic evenly and make sure your app is stateless so each instance can handle requests independently.
Which is right for my app: Horizontal vs. vertical scaling?
You need horizontal scaling if your app has to handle high traffic and support many users, or requires high availability, especially in cloud environments. Furthermore, you require vertical scaling if you are looking to build a simple app where upgrading a single server is enough. In simple terms, if you frequently experience high traffic spikes or require fault tolerance, then horizontal scaling is the better and long-term choice.
How does horizontal scaling work in cloud computing?
Horizontal scaling works in cloud computing by the addition or removal of virtual machine instances or containers (based on demand). A load balancer distributes the incoming traffic across these instances. This ensures that no single node is overwhelmed. Moreover, you can also automatically adjust the number of instances to optimize cost with the help of cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and GCP.
What are the challenges in the implementation of horizontal scalability?
Other than cost, some of the common challenges you can come across in implementing horizontal scaling are given below:
- Ensuring your app is stateless or uses external sessions.
- Managing synchronization across distributed databases.
- Correct distribution of traffic to avoid bottlenecks.
- Monitoring of debugging issues across multiple instances.
Why is statelessness critical in horizontally scalable apps?
It is critical in any horizontally scalable app because it allows any instance of the application to handle any request independently. Also, no session data is stored on a specific server, so requests can be freely distributed across multiple nodes using a load balancer.
What are the key architectural components for horizontal scalability?
The key architectural components that make horizontal scalability possible are given below:
- Load Balancer
- Stateless Application Layer
- Distributed Databases or Shading
- Caching Systems
- Auto-Scaling Mechanisms
- Message Queues
- Centralized Monitoring and Logging


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 August 11 2025
August 11 2025