Healthcare is more connected than ever, but this connection can fall apart without secure communication between systems. That’s where interoperability is key, ensuring secure data transfer between multiple systems. The healthcare industry is witnessing a rapid shift due to technological advancements, and we are seeing diverse interoperability use cases emerge, such as telehealth, remote monitoring of patients, and EHR-to-EHR data transfer. In this blog, we will tell you all about how interoperability serves the healthcare industry.
Interoperability Use Cases in Healthcare
The healthcare industry has multiple data exchange architectures and standards. Here, interoperability can be helpful in the smooth transmission and interpretation of data. Right now, we are highlighting the top three use cases of interoperability, and we will share more, so keep reading.
- Interoperability allows hospitals or clinics to safely extract patient records while keeping all the detailed, structured information intact.
- Interoperability makes ICU treatment safer and more efficient by reducing the need for manual intervention. With easy access to data, healthcare professionals can swiftly verify patient records and provide due care in time.
- Any authorized healthcare institution can transfer a portion or the complete patient record to another institution that uses a different EHR.
- Telehealth integration allows real-time data sharing between traditional healthcare systems and virtual care platforms. This allows better care coordination and detailed documentation.
After reading these applications, you are wondering why interoperability is so important. Then let us break down the concept of interoperability and why it’s crucial from the provider and patient’s perspective.
What is Healthcare Interoperability, and Why is it Important?
The interoperability in healthcare is the secure integration and access of electronic health data, which can be utilized to optimize health outcomes. In simple words, systems or devices can exchange and use information from other devices without any special effort.
In short, interoperability helps clinicians and hospitals provide safe, effective, patient-centered care. Now, let’s move on to why healthcare interoperability is crucial. We are dividing it into two perspectives for better understanding.
Importance of Interoperability
In healthcare, interoperability is crucial because patients receive treatment from various providers across multiple healthcare systems. Interoperable systems support effective and coordinated care.
- Patient Perspective: A patient may get care from different providers working in various healthcare systems, and can be on numerous payer panels. Here, interoperability can help enhance patient care by providing an overview of patient health data such as allergies, history of past diseases, treatments, medications, financial claims, etc.
- Provider’s Perspective: From the provider’s perspective, interoperability can help providers exchange and access patient data faster, anywhere and anytime in a standardized form. This helps reduce errors, saves time, and enhances communication among care teams.
The interoperability improves the collaboration between insurance companies and healthcare providers. Thus, removing the barriers and offering smooth data flow between stakeholders for enhanced patient care. With the rise in collaborative care, seamless data flow is required, making systems interoperable helps.
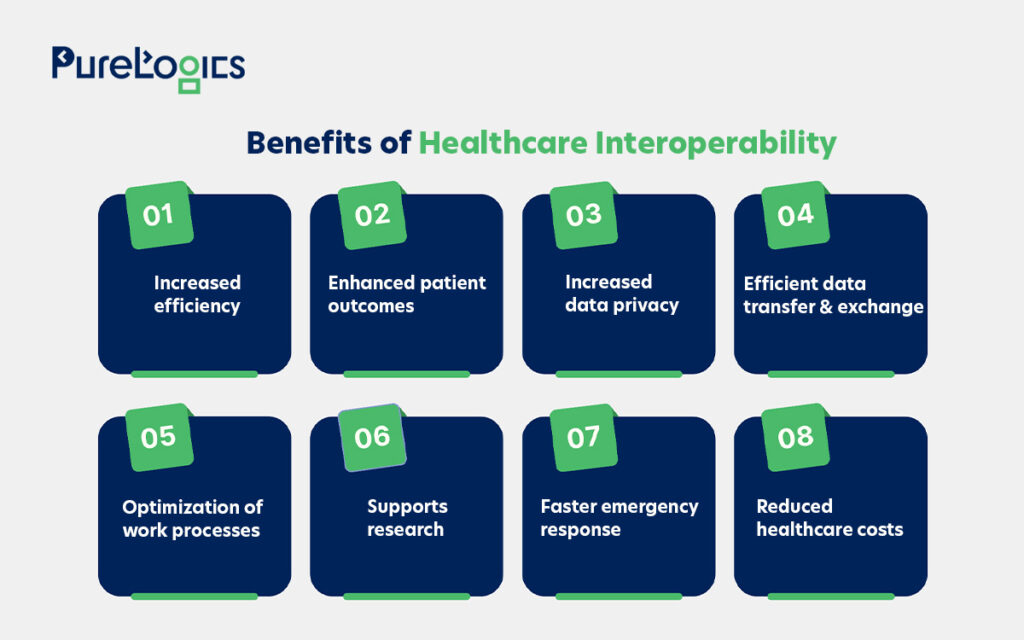
Benefits of Interoperability
Interoperability improves care quality, increases efficiency, and enhances patient outcomes. It also provides timely access to critical health information. Some other top advantages of interoperability are given below:
Before moving to interoperability use cases, let’s discuss interoperability levels so you can fully comprehend everything.
Levels of Healthcare Interoperability
To understand interoperability use cases completely, you first have to understand the levels of interoperability.
| Foundational | Structural | Semantic | Organizational |
| The foundational level is the initial one that defines the basic standards for a system or app to communicate securely. For example a nurse downloads the PDF file of the patient’s latest lab results and manually enters data into the patient’s health records. | This level explains the organization, syntax, and format of data structuring, making it easy for multiple devices and systems to interpret data. | Semantic allows the interpretation of data for use in clinical decision making.For example, many DICOM and non-DICOM formats for images with semantic interoperability can be interpreted and inserted into new systems (regardless of size and format). | It allows smooth data transference, keeping the organizational, legal, and policy requirements in view. |
Interoperability is impossible without standardized data transfer, and there are different standards. Let us define these standards, too.
Standards of Healthcare Interoperability
These standards lay the foundation of interoperability use cases by allowing safe data transfer between systems.

Here’s a brief description of all standards.
HL7
It is a standard and messaging format that is used to exchange data between healthcare systems. In addition to secure data exchange, there are multiple reasons HL7 is required.
HL7 has different versions that help in promoting interoperability.
HL7 v2
The purpose behind HL7 v2 was the exchange of message-based healthcare data. It helps in smooth communication between healthcare apps and systems. This version uses delimited text messages with separators like (|) and carets (^), and its flexibility allows organizations to meet their unique needs.
The next one we have is v3, which was released in 2003.
HL7 v3
It covers different aspects such as data types and terminologies. This version has a semantic approach and is more widely used than v2. Some of the notable features of this version are below:
- It is easy to implement and flexible.
- This version utilizes a structured approach for data exchange.
- The web standards, XML, JSON, and HTTP make it more interoperable.
The next one is HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), combining the best v2 and v3.
HL7 FHIR Standard
FHIR is free, and the primary purpose behind its implementation is API-driven healthcare data exchange. The importance of FHIR cannot be denied, and some of its features are given below:
- It utilizes RESTful APIs, which allow efficient data exchange.
- Designed for easy and fast adoption.
- Uses web standards like XML and JSON.
FHIR is suitable for modern healthcare systems and has extensive resources.
HL7 CDA
CDA stands for Clinical Document Architecture. It is an electronic standard for clinical data exchange. Some of its top features are given below:
- It is an XML-based standard.
- HL7 CDA ensures human readability and machine processability.
- Allows structured exchange of data.
HL7 CDA is highly flexible and highlights the structure and semantics of clinical documents.
Now let’s move on to HIPAA, which deals with protected health information (PHI).
HIPAA
The HIPAA stands for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act and aims to protect sensitive patient health information (PHI). Companies dealing with PHI must have physical and procedural security networks to ensure HIPAA compliance. It is not just a standard to ensure security but to promote interoperability.

With a clear understanding of the standards that make data exchange possible, we can now look at how interoperability helps the healthcare industry.
Interoperability is not just a technical goal; it shows up in practical ways across the healthcare industry every day. From scheduling a virtual visit to data transfer between EHRs, the following interoperability use cases define this sector.
Top Interoperability Use Cases in Healthcare
Interoperability is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity to streamline communication between healthcare systems. Below are some of the most popular use cases of interoperability.
1. EHR to EHR Data Sharing
The first in the interoperability use case is data transfer from one EHR to another, also known as EHR interoperability. Different EHR systems can exchange information safely. This helps the healthcare providers exchange data and, at the same time, get secure access to patients’ comprehensive health records even if the patient data is present in a different EHR system. Let us give you an example: a patient schedules an appointment at a new clinic, and a doctor wants access to the patient’s history, such as previous medications, lab results, and allergies. The doctor now has three options here:
- Request access to medical documents from the patient’s previous clinic.
- Demand that the patient procure the health records.
- Repeat the lab test.
The options mentioned above are undoubtedly inefficient, especially in terms of resource utilization and time management. However, in contrast, the software or platform that runs by interoperability standards can help safely and efficiently transfer data.
For instance, the physician can also request a longitudinal view of the patient’s treatment in different hospitals. This efficiently helps doctors in the prior planning of treatment and preparation of medication schedules.
Furthermore, due to interoperability, the doctors do not require the physical presence of patients to plan their treatments. They can do it with the help of imaging files and copies of the EHR.
2. Telehealth
Telehealth is one of the key examples of interoperability in healthcare. It allows for the smooth exchange of patient data between online doctor visits and hospitals or clinics. This ensures that all healthcare providers have the exact details so that a patient gets better care without delay. For example, the data from video consultations and remote assessments can be sent securely to the EHRs, ensuring continuous care. It also enables the providers to make informed decisions and maintain a complete and up-to-date patient record.
3. Scheduling Software
The scheduling software allows patients to schedule their appointments while safeguarding the patient and providers’ information and ensuring that sensitive health data is stored and transferred. All because of interoperability.These software share:
- Patient information like name, contact, and ID.
- Appointment details such as time, provider info, and type of service.
- Provider’s availability and care plans (if integrated with EHRs).
- Reminders and confirmation (through messaging systems).
Let us give you an example of one of our projects, CaringonDemand, a HIPAA-compliant iOS-based app that connects people who need care with nearby providers.
The following features of the software make it smooth and seamless.
- Safeguards patient and provider information.
- Secure transfer of healthcare data as per HIPAA guidelines.
- Allows real-time matching between care providers and recipients.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring is one of the most famous interoperability use cases. It allows remote monitoring devices like glucose meters or pressure cuffs to transfer real-time patient data to EHRs (Electronic Health Records). For instance, a cardiologist can get the heart rate daily from a patient’s wearable device and send it to EHRs. Also, allowing for timely intervention without an in-person visit. This smooth data exchange enhances chronic care management, minimizing hospital readmissions, and improves clinical decision-making.
5. e-Prescription Software
Interoperability plays a key role in e-prescription software by allowing safe and smooth data exchange between healthcare providers, pharmacies, and EHR systems. It helps doctors send prescriptions directly to pharmacies in real time, reducing errors, delays, and paperwork.
With access to complete patient records, including medication history and allergies, the e-prescribing systems help ensure safer and more accurate prescriptions. The interoperability also supports features like:
- Authorization.
- Instant insurance checks.
- An efficient medication approval.
To ensure the safety of the patient data, safeguards like encryption, access controls, and audit logging are included. Let us give you an example of e-prescription software, which we developed for one of our numerous clients. It addresses the unique needs of healthcare providers and professionals. With separate logins for patients and doctors, an easy-to-use interface compatible with each device.
6. ICU System Integration
In critical care settings like Intensive Care Units (ICUs), timely and accurate information is vital. Interoperability allows efficient data exchange between ventilators, infusion pumps, monitors, and lab systems. This structured data flow allows doctors or clinicians to monitor patient status, respond rapidly to fluctuations, and promote efficient coordination between departments. It also reduces manual data entry and the risk of errors, ultimately enhancing patient safety and outcomes. This is one of the most effective and practical interoperability use cases in healthcare.
AI in Healthcare Interoperability
Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare is essential in mitigating the challenges associated with interoperability. Heres how
- Data Mapping
AI algorithms can translate and process data to make it compatible for smooth exchange from one system to another. This power to map and transform the data makes connecting with previously incompatible systems easy.
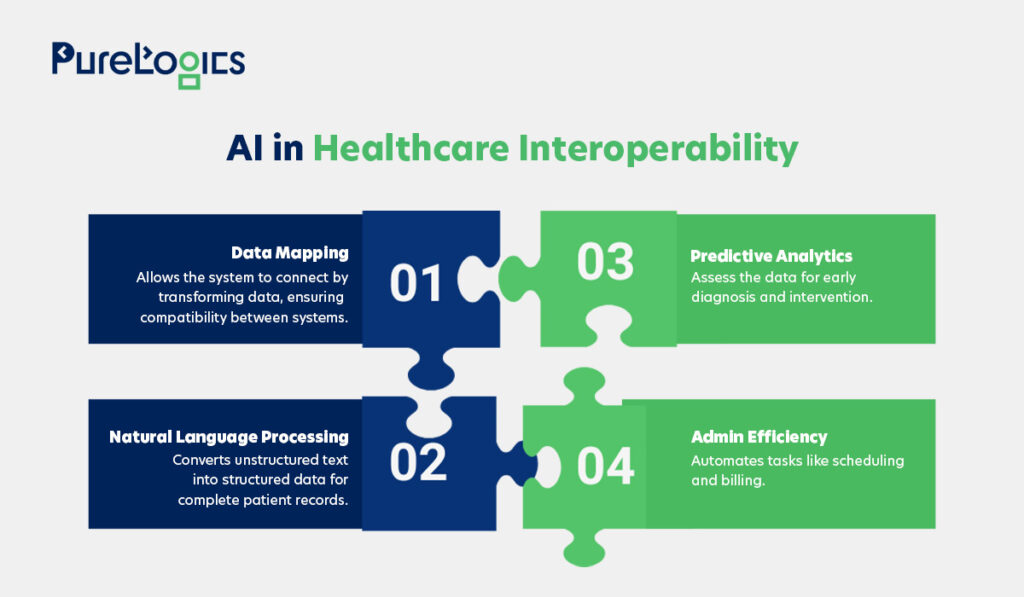
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This technology allows the AI to extract meaningful information from unstructured data sources, such as clinical notes. This enables healthcare providers to create and preserve comprehensive patient records.
- Administrative Processes
AI tools can streamline the administrative tasks in healthcare, from managing billing to scheduling appointments. Here, the interoperability between administrative systems results in more efficient healthcare operations.
- Predictive Analytics
AI uses data to predict health risks, possible outcomes, and patient needs. With interoperability, doctors can gather data from multiple sources like EHRs, wearables, and labs to fully view patient health. This can help them identify warning signs to prevent further complications, delivering more personalized care.
Conclusion
Interoperability is not just another tech trend; it is the backbone of modern healthcare. Whether it’s data exchange between EHRs, telehealth, or remote monitoring of patients that updates patient health records in real-time, each of these interoperability use cases brings us closer to more efficient healthcare systems.
With around two decades of experience in healthcare software development, PureLogics has helped healthcare providers worldwide build HIPAA-compliant software supporting interoperability with secure and smooth data exchange. Contact our healthcare IT professionals and share your digital healthcare project idea today!


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 June 23 2025
June 23 2025