Teams strive for different methods that enhance project management flexibility, efficiency, and productivity. Agile methodologies have become a guide to adaptability in this market, with Scrum and Kanban leading the way.
Both frameworks have common agile origins, emphasizing team collaboration, customer satisfaction, and incremental work. However, their methodologies to achieve these goals vary and are customized to suit team dynamics and unique project requirements.
Defining Kanban and Scrum: What Sets Them Apart?
Both Kanban and Scrum are popular Agile methodologies designed to improve efficiency and flexibility in project management. However, they differ in several key aspects, from their structure to how they manage workflow and handle change.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is an Agile methodology built for complicated projects where adapting to change is frequently required. It is established on short development cycles known as sprints, which normally last one to four weeks. A scrum team is autonomous and small, with one scrum master and a product owner. The remaining team is known as the development team.
Scrum utilizes an iterative approach to project completion as the standard agile framework. This ensures ease of adaption to evolving priorities and changes.
Core components of Scrum
Scrum is based on three core components:
1: Adaptation: Scrum is adaptive, meaning it can embrace any changes and seamlessly handle a project’s changing strategic directions.
2: Inspection: Stakeholders and team members examine projects consistently. This empowers a culture of advancements.
3: Transparency: Transparency ensures all team members know what’s happening during the projects and why.
Scrum has five core values: focus, respect, commitment, courage, and openness. These values emphasize the importance of transparent communication and a sense of ownership by all team members.
Need Help Navigating Agile Frameworks?
Our experts can tailor the perfect solution to your project’s unique demands.
What is Kanban?
This visual approach to project management is utilized to monitor tasks and minimize inefficiencies. The main part of the Kanban approach is the Kanban board—digital or physical—in which project phases are divided into various columns. Tasks are described on cards that advance from one column to the next until given tasks are finished.
Kanban boosts transparency within a project by visually clearing what tasks must be completed and where they are piling up. Using this visual aid makes assigning resources where they should go easier, minimizing inefficiencies. Based on the 2022 State of Kanban Report, the top benefits of Kanban include:
- Enhanced flow visibility
- Improved predictability
- Higher throughput/delivery speed
- Better alignment within business objectives, work delivery, and key results
Kanban utilizes principles from both Lean and Agile. It can be used seamlessly with various other methodologies and is normally utilized in tandem with Scrum within a hybrid procedure called Scrumban. Based on the 2022 State of Agile report, around 27% of survey participants used Scrumban, while 56% used Kanban.

Core components of Kanban
Here are the core components of Kanban:
1. Kaizen: Kaizen means “improvement” and encourages the approach to enhance the process continually. It also allows team members to share their work and insights to improve team dynamics, not just the managers.
2. Definition of Workflow: This defines key aspects of the Kanban workflow, like what units are moving via the board, what “initiated” or “completed” means, and how long an item must advance through the columns.
3. Work in Progress limits: All teams can set WIP restrictions in a column, entire board, or groups of columns. It means a column with a WIP limit of six can’t have more than six cards in it at a time. Work-in-progress limits can assist surface problems in the production procedure.
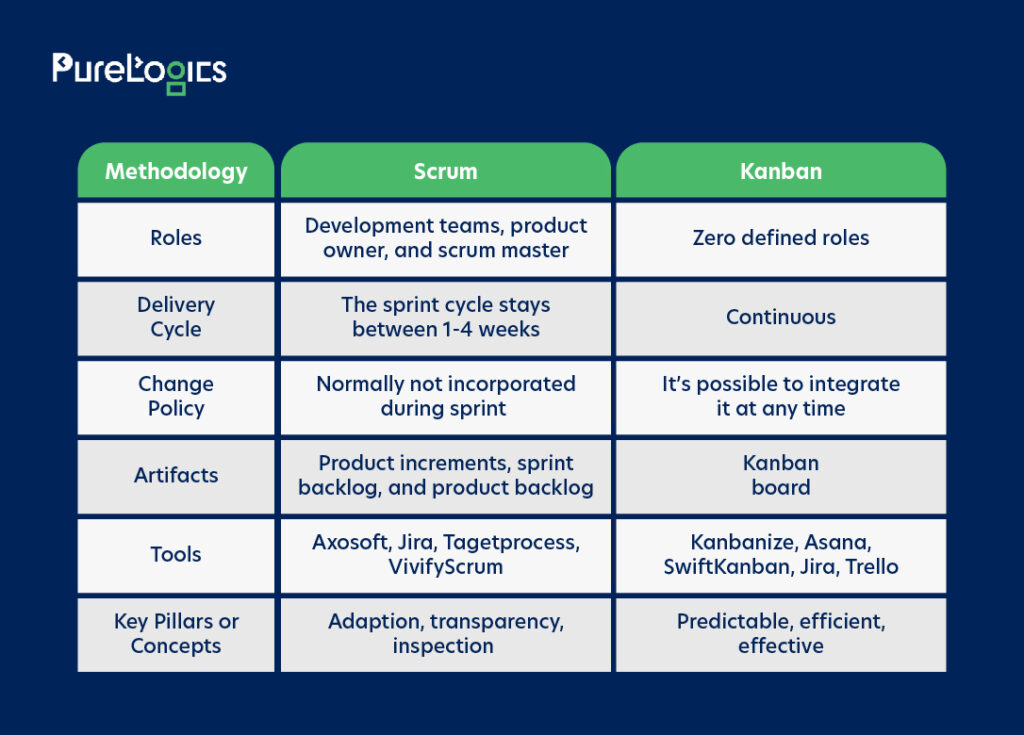
Scrum and Kanban: Comparing Similarities and Differences
The differences and similarities between Scrum and Kanban can be synopsized as follows:
- Scrum and Kanban can let projects adapt to change, empowering engagement by team members, increasing transparency, and having small development cycles.
- Scrum is a procedure that structures team culture and workflows to provide projects quickly, while Kanban is a methodology focused on visualizing tasks.
- Scrum offers parts of deliverables in one to four weeks, while Kanban delivers processes continuously till the project is completed.
Take a look at the side-by-side comparison of Scrum vs. Kanban:
Kanban vs. Agile
Agile is a group of project management principles that empower an iterative and adaptive approach to project management. It’s an overarching dilemma and not a set of processes or tools. It provides flexibility in following a plan and is normally utilized for projects that need frequent changes.
On the other hand, Kanban is an Agile methodology. It provides the specific processes and tools needed to implement Agile. It showcases Agile principles and key points, such as transparency across teams and the capacity to adapt to updates.
Kanban vs. Waterfall
Waterfall is a relatively traditional method of project management where tasks are completed in a predefined order until its completion; as water might fall as a series of rocks within a Waterfall, it’s not designed to adapt to changes throughout a project and is suggested for projects where a small number of changes are expected. This includes projects that have time constraints or strict budgets or where processes must be finished sequentially.
The waterfall isn’t as flexible as Kanban because it has a higher capacity to adapt to changes. However, project managers can visualize tasks using an adapted Kanban board within a Waterfall procedure.
Scrum vs. Kanban: Deciding the Right Fit
Scrum vs. Kanban has its strengths, but putting Kanban against Scrum is not right because you can easily utilize both in your business to maximize profit.
When to go with Scrum
Scrum has been connected to faster delivery, higher quality, productivity, and lower costs. Multiple project managers also consider Scrum an efficient way to handle complex projects. It’s best to use if you’re in an industry where frequent change is required or if the project needs the capacity to adapt to feedback. Additionally, Scrum includes industries that have projects building new products and frequent technology updates.
When to go with Kanban
Kanban is best for enhancing visibility, maintaining a culture of continuous updates, and boosting productivity. It can fit in with tasks that currently exist, including Scrum. Kanban is the way to go if you want to avoid overhauling your entire workforce but hope to get the benefits of an Agile project.
Scrumban: Selecting Both
Scrumban is a hybrid approach that gathers both Scrum and Kanban. It utilizes the visualization tools of Kanban and tasks of Scrum. Scrumban is an ideal way for conventional teams with Kanban or Scrum to implement the other into their tasks.
Overwhelmed by Choosing the Right Agile Framework?
Let our experts guide you in implementing the perfect methodology for your web development projects.
Conclusion
Each framework provides its own set of benefits and considerations. While Scrum offers efficiency and structure for huge, long-term projects, Kanban provides adaptability and flexibility for ongoing task flows, ensuring it is suitable for engineering, development, and manufacturing teams. On the other hand, Scrumban has elements from Scrum and Kanban, ensuring a balance between flexibility and structure, making it a great option for evolving environments like startups.
Still confused about making the right call? Let PureLogics’ experts handle this. We have 20+ years of experience+ years in web development services. We understand there’s no one-size-fit solution for everyone, so we assess your unique project needs and build an agile methodology that gives you higher efficiency, flexibility, and productivity. Give us a call today!


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 October 7 2024
October 7 2024






