According to international reports, spatial computing will have a market size of more than $700 billion by the end of 2033. Spatial computing integrates artificial intelligence, computer vision, augmented reality, and virtual reality to bring virtual experiences into our physical world. Tech experts believe that spatial computing technology will influence the world just like smartphones impacted the world in the 2000s.
With this amazing technology, your surroundings will be interactive canvases. It creates an environment where every gesture of canvas will reinvent your digital interaction. Spatial computing is a technology that significantly influences customer engagement and provides personalized experience for every individual.
But what’s the game-changer here for your industry?
With a creative and experienced team of 400+ minds at PureLogics, we have multiple perspectives on the transformative potential of spatial computing. From healthcare and e-commerce to fashion and music, we see endless possibilities for innovation across industries.
This blog post will give you hot insights into the future of spatial computing. Here, you will explore applications of spatial computing and its potential to bring revolution in user experiences. So, without further ado, let’s dive into the details!
What is Spatial Computing?
Spatial computing refers to the use of digital technologies to interact with the physical world in real-time. By merging the digital and physical realms, it allows users to interact with data and virtual objects in a 3D space. This advanced computing approach relies heavily on technologies like AI, AR, VR, and IoT, offering seamless integration between the real and digital environments.
Applications of Spatial Computing
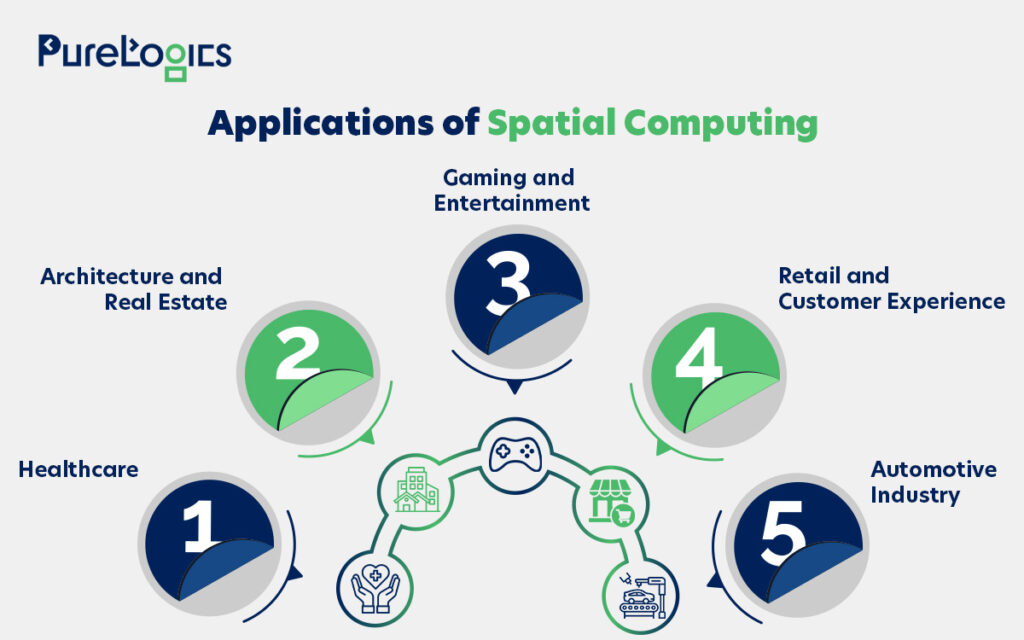
Now, let’s examine applications of spatial computing!
Healthcare
Spatial computing is revolutionizing healthcare by improving patient care and streamlining medical practices. Augmented reality (AR) is being used for surgical planning and training, helping doctors visualize complex surgeries before they even begin.
It also aids in medical imaging, allowing professionals to view 3D models of organs and tissues, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and precision. Virtual reality (VR) is also becoming a tool for pain management, offering patients an immersive escape during treatments.
Architecture and Real Estate
Architects and real estate professionals are using spatial computing to create virtual walkthroughs of buildings and properties. This helps clients visualize how spaces will look once constructed, enabling better decision-making during the design phase.
In real estate, spatial computing provides potential buyers with virtual property tours, making it easier for them to explore listings remotely.
Gaming and Entertainment
Gaming has been one of the most prominent sectors benefiting from spatial computing. Virtual reality (VR) gaming, in particular, offers an immersive, interactive experience that transports players into entirely new worlds.
Augmented reality (AR) also plays a key role in gaming, allowing for more interactive experiences that combine physical and digital elements. Beyond gaming, spatial computing is reshaping entertainment, including live concerts, performances, and events, by enabling new ways to experience and interact with media.
Retail and Customer Experience
In retail, spatial computing helps improve customer experiences both online and in-store. For instance, AR can be used to create interactive advertisements and displays that allow customers to explore products in detail.
In physical stores, spatial computing can provide personalized recommendations based on a customer’s location within the store, creating a more tailored shopping experience.
Automotive Industry
Spatial computing is transforming the automotive industry by enabling the development of autonomous vehicles and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Through sensor technology, real-time mapping, and computer vision, self-driving cars are able to understand their surroundings, navigate safely, and make split-second decisions based on their environment.
How Spatial Computing is Shaping the Future of Business
As the world becomes more interconnected, spatial computing is offering new opportunities for businesses to innovate and improve their operations. Here are some key ways in which spatial computing is shaping the future of business:
Enhanced Customer Engagement
One of the primary ways that spatial computing impacts businesses is by enhancing customer engagement. By integrating AR, VR, and AI, companies can provide interactive experiences that capture users’ attention and provide them with unique and personalized content.
Whether it’s a virtual fitting room or a VR simulation of a product in action, spatial computing offers customers a chance to interact with brands in ways that were never before possible.
Improved Productivity and Efficiency
Spatial computing helps businesses streamline their operations and improve efficiency. For example, in the manufacturing industry, AR can be used to guide workers through complex tasks, reducing the time it takes to train employees and increasing productivity.
In logistics, spatial computing enables real-time inventory tracking and warehouse management, reducing errors and improving order fulfillment times.
New Business Models
Spatial computing also opens up the door to entirely new business models. From virtual stores in the metaverse to immersive product demonstrations in augmented reality, businesses can explore innovative ways to engage with customers and generate revenue.
This technology allows for the creation of entirely new consumer experiences that bridge the gap between physical and digital environments.
Comparison of Spatial Computing and Similar Technologies
| Feature | Spatial Computing | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
| Primary Focus | Interaction between physical and digital worlds | Overlaying digital content on the real world | Fully immersive simulated environments | Machine learning and automation |
| Technologies Used | AR, VR, AI, Computer Vision | AR, Computer Vision | VR, Computer Graphics | AI Algorithms, Neural Networks |
| User Interaction | Real-time interaction with physical surroundings | Interaction with digital objects in the real world | Complete immersion in a digital world | Automation and decision-making |
| Immersion Level | Medium (blends physical and virtual) | Low (overlayed content) | High (immersive experiences) | Medium (no physical interaction) |
| Use Cases | Healthcare, retail, gaming, architecture, education | Retail, gaming, marketing | Gaming, training, simulations | Healthcare, automation, customer service |
| Hardware Requirements | Wearable devices, sensors, cameras | Mobile devices, AR glasses | VR headsets, motion sensors | Servers, computing devices |
| Real-World Integration | High (combines digital and physical spaces) | Medium (adds digital to real world) | Low (entirely virtual world) | Low (no physical world interaction) |
| Cost | High (requires multiple technologies) | Low (simple hardware requirements) | High (requires VR headset) | Varies (depends on use case) |
| Complexity | High (requires advanced hardware and software) | Medium (simpler technology) | High (immersive tech with high specs) | Medium (depends on AI application) |
Final Remarks
Spatial computing is a groundbreaking technology that is shaping the future of business by enabling more immersive, interactive, and personalized experiences. From revolutionizing healthcare and retail to transforming education and manufacturing, its potential is vast and continues to grow. As the technology continues to evolve, businesses that embrace spatial computing will undoubtedly lead the charge in innovation.
At PureLogics, we specialize in helping businesses navigate this exciting frontier with cutting-edge spatial computing solutions. Contact us today to discover how we can help you unlock the full potential of this transformative technology!


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 March 26 2025
March 26 2025