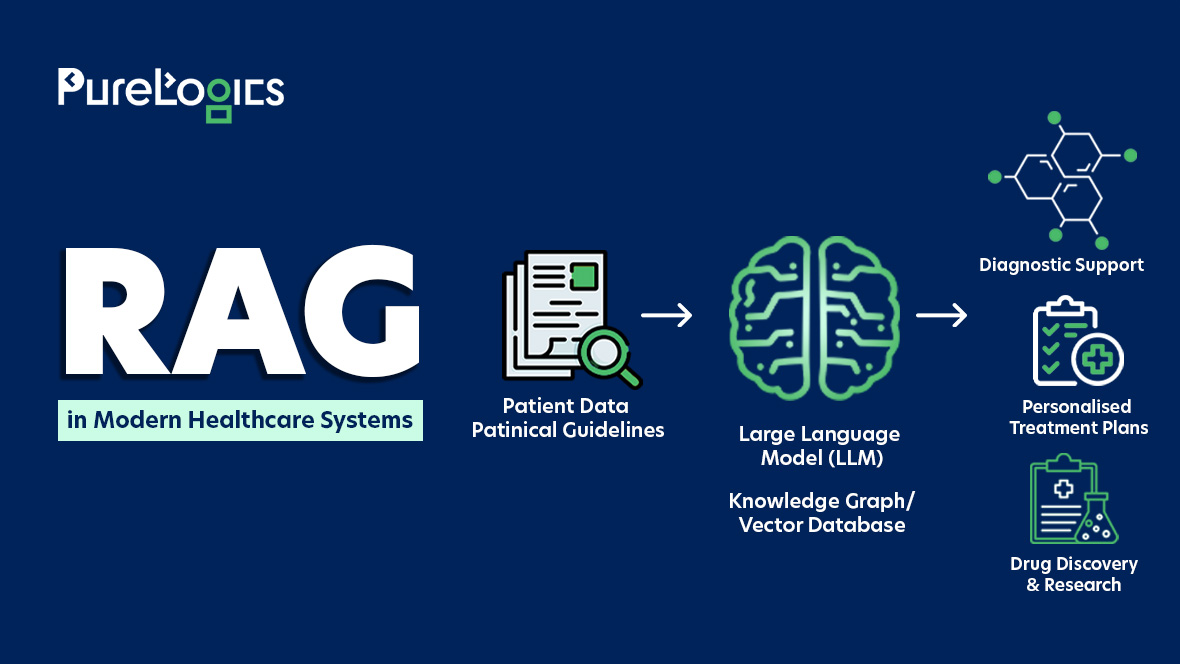
In 2025, as healthcare becomes more digital, the ability for systems to communicate and share patient information is more crucial than ever. Whether it is a hospital, clinic, lab, or telehealth platform, all healthcare providers must work together, which is possible through interoperability standards. They define how health data is transferred and understood across different systems.
In this blog post, we will break down the key standards that define healthcare in 2025, including HL7, FHIR, DICOM, and coding systems like SNOMED CT and ICD. These standards are divided into three categories:
- Messaging standards.
- Terminology standards.
- Clinical documentation standards.
Understanding these standards can help you reduce costs and streamline relevant administrative tasks. So, let’s get started with a brief introduction to interoperability standards.
What are Interoperability Standards?
The healthcare system is complex, and different types of software with distinct features are used to ensure patient care in hospitals and clinics. However, constant data exchange is also required internally and externally, which is why interoperability standards are needed. They provide a secure and efficient exchange of health information. The main goal here is the exchange of data safely and securely.
Three Interoperability Standards
The three main groups in which healthcare data exchange standards are divided are given below:
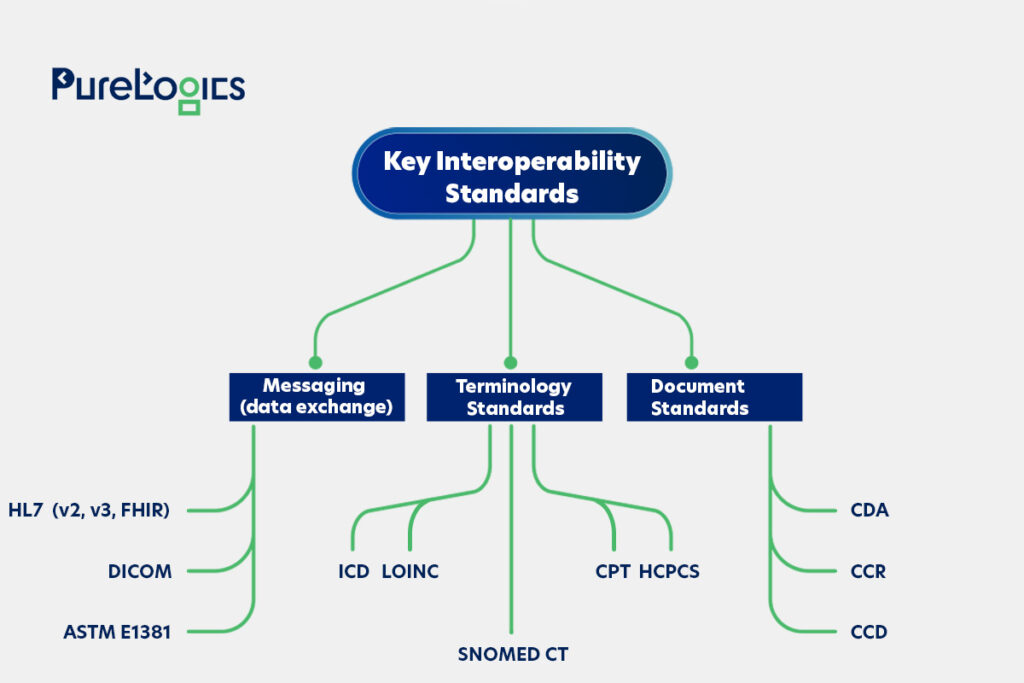
Despite having these standards, 30% of HIEs reported not knowing if the information they have transmitted or received complies with USCDI’s semantic standards, which shows the lack of awareness.
Keep on reading because we are going to define the different standards of interoperability mentioned above. This will help you understand the importance of these standards, starting with the first one, Messaging.
Messaging Standards
Messaging (or data exchange) standards ensure the consistent exchange of information between systems. The main goal is to define instructions for the data types, formats, and structures. So that all systems have common rules for clinical information exchange.
HL7 standard and DICOM are the most widely used standards. Let’s discuss the first type, which is HL7.
1. Health Level 7 (HL7)
HL7 is an international standard and messaging format used for data exchange between healthcare systems. It has different versions that facilitate the secure and swift data transmission for healthcare institutions. The types of messaging standards are given below:
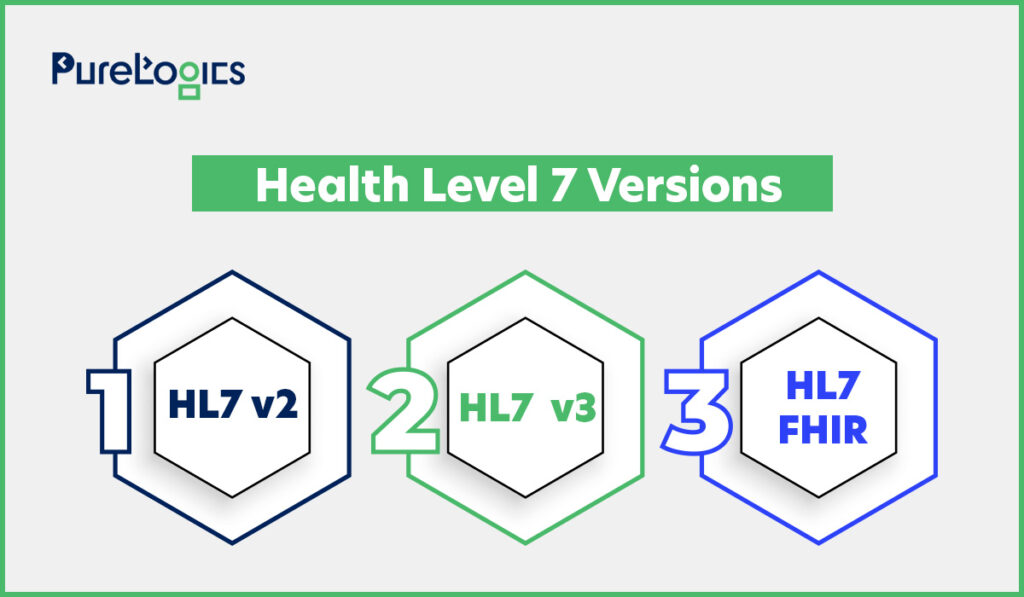
The different versions of HL7 are for integrating, transferring, and receiving data. However, the v2 is divided into 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.3.1, 2.4, 2.5, 2.5.1, and 2.6. Each version has more message types and features, making this standard more complex and robust. The v2.3.1 and v2.5.1 are the most used ones.
In short, HL7 offers a set of standards for transferring, integrating, and retrieving electronic health information. HL7 also helps in automating tasks with a variety of other advantages. Below, let’s discuss version 2 (v2).
- HL7 Interoperability Standard v2
Introduced in the 1980s, the main aim of this standard is to exchange message-based healthcare data. It streamlines communication between healthcare apps and systems, such as laboratory and billing systems. The key features of this version are given below:
- It uses delimited text messages with separators like (|) and carets (^).
- The v2 flexibility enables customization to meet the organization’s unique needs.
The next version is HL7 v3, which was released to mitigate integration challenges associated with v2.
- HL7 v3
Version 3 of the HL7 interoperability standard was released in 2003 and covers aspects related to implementation, such as messaging, data types, and terminologies.
It is based on RIM (Reference Information Model), which guides how clinical data is structured and exchanged within clinical activity (throughout different stages of patient care). This version has a semantic approach and is more widely used than v2, which is strict. The features of this version are given below:
- It is flexible and easy to implement.
- The v3 utilizes a structured approach to data exchange.
- More interoperable due to web standards (XML, JSON, and HTTP).
This version has a model-driven approach with a focus on interoperability and data consistency.
- HL7 FHIR Standard
FHIR combines the best of HL7 v2 and v3, and it uses web standards like XML and JSON to focus on implementation. It is free and can be used without any restrictions, and the primary purpose behind its generation was API-driven healthcare data exchange. Its importance in the healthcare system cannot be denied. Some of its top features are given below:
- FHIR utilizes RESTful APIs, which enable efficient exchange of data.
- It supports both JSON and XML data formats, providing flexibility.
- It is designed for fast and easy adoption.
FHIR has extensive resources, making it user-friendly and suitable for modern healthcare systems.
- SMART on FHIR
SMART stands for Substitutable Medical Applications and Reusable Technologies, and SMART on FHIR is a set of open standards and specifications that work together to offer means that help healthcare IT professionals to develop and smoothly integrate healthcare apps.
The latest technologies, such as OAuth 2.0 for safe authentication and RESTful APIs for data exchange, are used.
The developers can create healthcare apps that safely authorize and communicate with EHRs and other healthcare data sources by following this approach. And the apps built on this framework can easily be integrated with various EHRs without custom integrations.
The next one on our list of interoperability standards is DICOM, which is for the safe exchange of medical images.
2. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)
It is an international standard that specifies the protocols utilized to facilitate the exchange of medical images and other data related to healthcare systems. DICOM defines the file formats and assists in efficient workflows in image-capturing processes (like X-rays). Also, it has a built-in communication protocol and supports TCP/IP.
In short, DICOM allows the efficient handling, storage, printing, and transfer of medical images using DICOM files.
In DICOM’s jargon, the capture of a medical image is called acquisition, and imaging equipment units are called acquisition devices.
3. ASTM E1381
It is a key messaging standard for exchanging laboratory data between Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) and medical devices. Developed by ASTM International, based on the HL7 standard, it ensures interoperability and efficiency. The main features of ASTM E1381 are given below:
- The protocol can integrate with various devices, making it modular.
- It promotes interoperability, allowing different devices to communicate (there are some limitations concerning the modern environment).
- Provides a standardized structure for data transfer, ensuring consistent communication.
- Offers a basic error-handling mechanism that arises during data transmission.
After discussing interoperability standards, we are going to explain terminology standards.
- Terminology Standards
The terminology standards are the fundamental building blocks for standardizing health information, allowing accurate data exchange across different healthcare systems. The standardized codes and terms increase the efficiency of healthcare.
These interoperability standards offer specific vocabularies for clinical concepts such as diagnoses, diseases, and medications, which all systems understand. The most essential terminology standards are:

Let’s first start with SNOMED CT, which explains nearly all the concepts that can be used in medicine.
1. SNOMED CT
It aims to identify all concepts that can be used in medicine, and it stands for Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms. This terminology is distributed and maintained by SNOMED International. Currently, it is the richest vocabulary for coding clinical findings, diseases, and procedures, covering the entire spectrum of the health domain. It contains more than 300,000 concepts, and the ability to relate to them. The top features of SNOMED CT are given below:
- Comprehensive clinical terminology offering terms in multiple languages.
- Provides a consistent way to represent clinical data.
- It can be mapped to other health standards.
SNOMED supports the development of comprehensive, high-quality content in EHR (Electronic Health Records). The next one is ICD-11, which is mainly used for statistics.
2. ICD-11
It stands for the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and provides a comprehensive disease classification and coding. As well as a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, social circumstances, complaints, and external causes of injury or disease.
ICD was released by the World Health Organization (WHO), and ICD-11 is its 11th version. This interoperability standard is beneficial in collecting helpful health information related to death, diseases, and injuries. Some of the top features of the ICD are given below:
- Offers offline functionality.
- It allows more precise and detailed data collection.
- Gives disease classification data in multiple languages for integration in healthcare systems.
The next one is LOINC, which is utilized in coding laboratory results.
3. LOINC
LOINC stands for Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes and offers a complete classification of clinical observation in medicine. It is used to code laboratory results and is useful when an application must communicate with LIS (Laboratory Information Systems).
Since its origin, it has evolved and can be used to code physical examinations and other clinical observations. Some of the key features of LOINC are given below:
- LOINC is open and accessible to everyone.
- It facilitates the data exchange between different healthcare systems.
- Provides a unique code and name for each clinical observation.
The second last in the terminology standard is the CPT developed by the AMA.
4. CPT
It is a standardized healthcare interoperability standard for coding medical, surgical, and diagnostic procedures and services. CPT stands for Current Procedural Terminology and was developed by the American Medical Association (AMA). The top features of CPT are given below:
- Essential for billing and reimbursement of medical services.
- Codes are utilized to identify specific medical services and procedures.
- It improves the accuracy and streamlines claim processing.
CPT helps streamline reporting and increases efficiency and accuracy.
5. Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
It is a code set built by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) for reporting medical services and procedures. Here, the services and procedures have specified codes within the system to standardize medical billing.
- Clinical Documentation Standards
These standards, guidelines, and formats are utilized to record, structure, and share Patient Health Information consistently, correctly, and interoperably across healthcare systems.
You might think that messaging is enough for information exchange, but it is not because documents and messages have different characteristics. The documents can be signed, so they are legally valid. They include all necessary details about medical action and contain information that people, not just machines, can understand.
The examples of documents include discharge summaries, consultations, etc. The standards for CDA are:
1. HL7 CDA
Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) is an electronic standard developed by Health Level 7 for clinical data exchange. The top features of this standard are given below:
- It is an XML-based standard.
- This interoperability standard ensures human readability and machine processability.
- Enables structured data exchange, facilitating interoperability.
It highlights the semantics and structure of clinical documents. This standard is readable and highly flexible.
2. CCD
CCD stands for Continuity Care Document (CCD) and provides a core data set of the most relevant facts about patient healthcare data. Some of the top advantages of CCD, which make it popular, are given below:
- CCD offers all the details about patients, such as demographics, etc.
- It has a freeform text section, which is easily readable and enhances the meaning and accuracy of translation.
- It can be rendered as PDF and HTML, meaning there is no need for proprietary software or hardware to read.
In short, CCD offers a means for one healthcare practitioner to collect all vital information and send it to another so that the patients can get proper care.
3. CCR
CCR stands for Continuity of Care Record (CCR), an XML standard that summarizes the electronic health record (EHR) utilized for interoperability and exchanging patient records.
With the evolution of various standards, the Health Level Seven International (HL7) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) organizations coordinated on the Continuity of Care Document (CCD) to harmonize on the ASTM’s CCR with HL7’s Clinical Document Architecture (CDA).
Conclusion
With the evolution of the healthcare system, these standards no doubt have become essential for data exchange to provide collaborative care. Each standard can improve interoperability, from the foundational HL7 and FHIR to specialized SNOMED, CDA, and CCD. They also help healthcare providers and institutions offer data-driven care. Therefore, allowing them to enter the era of collaborative care.
At PureLogics, we understand that every standard serves a distinct role, and successful implementation depends on aligning them smoothly with technical infrastructure and workflows. So, contact our IT healthcare software developers for effective incorporation of these standards or the development of solutions based on them. With around two decades of experience, we are one of the leading healthcare software development companies. View one of our projects here.


 [tta_listen_btn]
[tta_listen_btn]
 May 26 2025
May 26 2025